Understanding the impact of digital transformation jobs
The difference between success and failure often comes down to leadership – and following a disciplined digital transformation approach can lift success rates from 30% to 80%.
Digital transformation roles create measurable business value by systematically connecting strategic vision to operational reality. Benefits Realization Management defines, plans, and tracks intended outcomes through benefits profiles, measures, and realization plans so transformation leaders can show the value they deliver against strategic objectives rather than just project outputs.
The financial impact of these transformation and change management professionals is significant. McKinsey’s State of AI report shows that organizations are achieving measurable cost decreases and revenue increases where AI is deployed.
Customer-centric metrics provide another lens on transformation value. Companies achieving high Net Promoter Scores grow revenues more than twice the rate of competitors, making NPS, retention, and customer lifetime value critical transformation KPIs for these roles.
Takeaway: Digital transformation jobs drive measurable business value by systematically connecting strategic intent to operational outcomes through structured benefits realization, customer experience improvements, and AI-enabled productivity gains.
What are the main responsibilities in digital transformation roles?
Digital transformation roles demand a blend of strategic vision, technical fluency, and operational discipline. These responsibilities span strategy formulation through execution and sustainment.
Core responsibilities center on value-driven execution:
- Digital Strategy: Define a clear, integrated digital strategy tied to measurable business value while securing leadership commitment and high-caliber talent to raise transformation success odds.
- User-Centered Delivery: Lead work to understand user needs, address the whole experience, and make services simple and intuitive by placing customer journeys at the center of transformation.
- Cross-Functional Leadership: Assign a single accountable leader and bring in experienced, cross-functional teams to execute the digital agenda at speed and scale.
- Cloud Foundations: Build cloud foundations across business, people, governance, platform, security, and operations to enable sustainable digital transformation.
- Modern Technology Stack: Choose a modern technology stack and adopt cloud platforms that support modular architectures, APIs, and scalable, reliable operations.
Technology enablement and automation drive efficiency:
- CI/CD Implementation: Automate testing and deployments through continuous integration and continuous delivery to improve release frequency, reliability, and quality across digital products and services.
- Hyperautomation: Drive hyperautomation using technologies like RPA and AI to automate as many business and IT processes as possible for efficiency and scale.
Risk management and security protect transformation investments:
- AI Governance: Govern AI adoption with risk management practices that address validity, safety, security, explainability, privacy, and fairness across the AI lifecycle.
- Cybersecurity Integration: Integrate cybersecurity and privacy into digital programs and advance a Zero Trust architecture to protect data, applications, and users.
Operational flexibility supports agile delivery:
- Agile Contracting: Structure budgets and contracts to support agile delivery and outcomes, enabling flexible vendor engagement and faster iteration.
Takeaway: Digital transformation responsibilities span strategic planning through operational execution, requiring leaders to orchestrate technology modernization, automation, security, and user-centered design while driving measurable business outcomes.
How do digital transformation jobs fit within organizational structures?
Digital transformation careers span diverse organizational structures, reflecting the enterprise-wide nature of these initiatives. Placement varies based on organizational maturity, transformation scope, and strategic priorities.
Executive-level positioning reflects strategic importance. Digital transformation is a CEO-level imperative that must be led from the top, signaling that core transformation roles typically sit close to the chief executive in the enterprise structure. The Chief Digital Officer leads enterprise digital business transformation and partners with CIOs and business leaders to deliver digital growth, reflecting a cross-enterprise mandate and C-suite proximity.
Centralized transformation offices orchestrate change. A transformation office acts as the enterprise control tower for change by aligning C-suite leaders, setting priorities, and driving cross-functional execution from the corporate center rather than within a single function. The Chief Transformation Officer partners with the CEO and board to orchestrate enterprise-wide change, typically by setting up and leading a central transformation office.
Cross-functional team structures enable delivery. Digital transformation practitioners often serve as individual contributors inside multidisciplinary fusion teams that blend business and technology expertise and share accountability for outcomes.
Takeaway: Digital transformation jobs typically sit at the corporate center close to the CEO, either within a centralized transformation office or embedded in cross-functional fusion teams, with reporting lines that enable enterprise-wide influence and coordination.
Key skills for digital transformation careers
Digital transformation careers require a distinctive combination of technical depth, strategic thinking, and change leadership capabilities that bridge business strategy with technology execution.
Technical and architectural competencies form the foundation:
- Cloud Adoption: Cloud adoption requires skills across architecture, security, operations, governance, and DevOps to build landing zones, manage, and secure workloads as core capabilities for scaling digital transformation.
- Enterprise Architecture: The TOGAF Standard provides a proven enterprise architecture method to align technology with business goals, a critical competency for governing complex digital transformations.
- Microservices and APIs: NIST guidance on microservices and service mesh architecture outlines patterns to build scalable, secure services through API and microservices skills that are key for modern digital platforms.
AI and data capabilities unlock value:
- AI/ML Operations: McKinsey reports rapid GenAI adoption and that organizations are putting in place model operations, monitoring, and governance, making the ability to build, deploy, and manage AI/ML systems a critical capability.
- Data Governance: Gartner’s 2024 data and analytics trends highlight delivering value with data governance, data sharing, and treating data as a product as essential capabilities to monetize and scale digital initiatives.
Security and privacy protect transformation investments:
- Zero Trust Architecture: CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model v2 guides implementation across identity, devices, networks, applications, and data through Zero Trust adoption that is foundational to secure digital modernization.
- Privacy Engineering: NIST’s Privacy Framework enables organizations to build privacy into products and services through governance, risk management, and engineering practices essential for compliant digital transformation.
Product and change leadership drive adoption:
- Product Management: SAFe 6.0 defines Product Management as owning vision, strategy, and the roadmap to deliver customer value as organizations shift from projects to products in digital transformations.
- Change Management: Projects with excellent change management are seven times more likely to meet or exceed objectives, highlighting the need to lead stakeholders through transformation.
Organizational capabilities enable execution:
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Deloitte’s 2024 Human Capital Trends emphasizes boundaryless, cross-functional work to adapt to constant disruption through collaboration and adaptability that are pivotal to transformation success.
Takeaway: Success in digital transformation careers requires mastering cloud architecture, AI/ML operations, data governance, and security while developing product management and change leadership skills that drive adoption and value realization.
What frameworks are critical in digital transformation jobs?
Digital transformation frameworks provide structured approaches to diagnose challenges, design solutions, and drive execution. Mastering multiple frameworks allows practitioners to apply the right methodology for each context.
Strategic and organizational frameworks guide transformation:
- Kotter’s 8-Step Process: Lead transformations by creating urgency, building a guiding coalition, crafting and communicating a vision, removing barriers, generating short-term wins, sustaining acceleration, and anchoring new behaviors.
- Team Topologies: Organize around stream-aligned, platform, enabling, and complicated-subsystem teams with defined interaction modes to improve flow of change and reduce cognitive load.
- RAPID Decision Model: Clarify who recommends, agrees, performs, inputs, and decides to speed cross-functional decisions and governance in transformation programs.
Agile and portfolio frameworks enable delivery:
- Scaled Agile Framework: Apply Scrum’s roles, events, and artifacts to deliver value in short cycles, enabling transparency, inspection, and adaptation for digital product and platform initiatives.
- Lean Portfolio Management: Align strategy to execution with Lean Portfolio Management by funding value streams, managing portfolio flow via Kanban, and governing with guardrails to prioritize digital initiatives by value.
Process improvement frameworks drive efficiency:
- Value Stream Mapping: Map end-to-end value streams to visualize information and material flow, identify waste, and design a future state that accelerates digital customer journeys and delivery pipelines.
- DMAIC Methodology: Improve digital-era processes with DMAIC through Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control to reduce defects, cycle time, and cost while increasing quality and customer value.
Customer-centric frameworks inform strategy:
- Jobs to Be Done: Discover customer jobs, pains, and gains to prioritize digital features and experiences that solve real problems and drive adoption and growth.
Change frameworks ensure adoption:
- ADKAR Model: Use ADKAR through Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, Reinforcement to systematically drive individual adoption and sustainment of new digital ways of working across the enterprise.
Takeaway: Proficiency across strategic frameworks like Kotter’s 8-Step Process, delivery frameworks like SAFe and Lean Portfolio Management, and process improvement tools like Value Stream Mapping enables practitioners to orchestrate complex digital transformations effectively.
Which tools are useful in digital transformation manager jobs?
Digital transformation manager jobs require proficiency across diverse software categories to orchestrate technology modernization, process automation, data management, and adoption tracking.
Cloud infrastructure and orchestration tools provide the foundation:
- Kubernetes: Open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Terraform: Infrastructure as code to provision and manage cloud and on-prem resources declaratively.
Integration and automation platforms connect systems:
- MuleSoft: iPaaS and API management to connect applications, data, and devices via reusable APIs and integrations.
- UiPath: End-to-end automation and RPA for automating business processes, with AI and process orchestration.
- Camunda: BPMN-based process orchestration for automating and coordinating human and system workflows across services.
Data platforms enable analytics and AI:
- Snowflake: Cloud data platform for secure data warehousing, lakehouse, collaboration, and governed data sharing.
- Fivetran: Managed ELT to extract data from SaaS and databases into cloud warehouses with automated connectors.
- Collibra: Data governance and catalog to define policies, steward data, and manage data lineage for compliance and trust.
Process intelligence informs optimization:
- Celonis: Process mining and intelligence to discover, visualize, and optimize processes using event data.
Adoption platforms accelerate user enablement:
- WalkMe: In-app guidance and analytics to accelerate software adoption and measure usage across enterprise applications.
Takeaway: Effective digital transformation requires proficiency across cloud infrastructure platforms like Kubernetes and Terraform, integration tools like MuleSoft and UiPath, data platforms like Snowflake, and adoption solutions like WalkMe to orchestrate end-to-end modernization.
Qualifications for digital transformation careers
Digital transformation careers typically require bachelor’s degrees in computer science, information systems, business administration, engineering, or related fields. Technical backgrounds provide foundational understanding of systems, data, and architecture that underpin transformation initiatives.
Advanced degrees strengthen strategic capabilities. Computer and information systems managers often central to digital transformation typically need a bachelor’s in computer or information science, with many also holding a graduate degree such as an MBA that combines technical depth with business acumen.
Specialized technical education supports platform roles. Computer network architects important for digital platform modernization typically need a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information systems, or engineering.
Professional experience often matters more than credentials alone. Employers value demonstrated success leading complex initiatives, managing cross-functional teams, and delivering measurable business outcomes. Many successful practitioners transition from technology leadership, program management, enterprise architecture, or digital strategy consulting roles.
Industry knowledge enhances effectiveness. Financial services organizations value understanding of regulatory requirements and risk management. Healthcare seeks familiarity with clinical workflows and compliance. Retail prioritizes omnichannel customer experience expertise.
Takeaway: Digital transformation careers typically require bachelor’s degrees in technical or business fields, with many senior practitioners holding advanced degrees, but demonstrated experience leading complex technology-enabled change initiatives often matters more than specific educational credentials.
What certifications benefit a digital transformation leader?
Professional certifications demonstrate expertise in specific methodologies and technologies critical to digital transformation success. Multiple certifications across different domains create well-rounded capability profiles.
Program and project management certifications provide delivery foundations:
- PMP Certification: Validates leadership experience and expertise in predictive, agile, and hybrid ways of working that are core for orchestrating complex digital transformation programs on scope, schedule, and budget.
Agile and scaled delivery credentials enable modern operating models:
- SAFe Agilist Certification: Prepares leaders to apply Lean-Agile principles and the Scaled Agile Framework to lead enterprise-scale transformations and align teams to value streams.
- ITIL 4 Foundation: Introduces a modern, end-to-end operating model for creating, delivering, and continually improving tech-enabled products and services as foundational for digital operating models.
Change management certifications drive adoption:
- Prosci Change Management Certification: Equips practitioners to apply Prosci’s methodology and the ADKAR Model to drive adoption and outcomes through the people side of digital transformation.
Product management credentials support customer-centric delivery:
- NPDP Certification: Validates mastery across product strategy, portfolio, process, and metrics that are vital for building and scaling digital products and services.
Process improvement certifications enhance operational excellence:
- Six Sigma Black Belt: Confirms ability to lead improvement projects using DMAIC and Lean methods for digitizing processes, reducing defects, and realizing measurable value.
Governance and risk management credentials ensure compliance:
- CGEIT Certification: Demonstrates expertise in governance of enterprise IT, ensuring technology investments align with business objectives and deliver value during transformation.
- COBIT 5 Certificate: Validates understanding of the COBIT framework for governance and management of enterprise IT for establishing controls and value delivery in digital programs.
Takeaway: Professional certifications in program management (PMP), agile delivery (SAFe), change management (Prosci), product management (NPDP), and governance (CGEIT, COBIT) create comprehensive capability profiles that distinguish digital transformation leaders.
Career paths in digital transformation jobs
Digital transformation offers diverse career trajectories with opportunities to specialize by industry, methodology, or organizational scope. Progression typically follows increased complexity, strategic influence, and leadership responsibility.
Typical career progression follows this pattern:
- Digital Transformation Analyst: Entry-level roles supporting data analysis, process documentation, and project coordination
- Digital Transformation Consultant: Mid-level practitioners leading specific workstreams or initiatives
- Senior Digital Transformation Manager: Experienced professionals managing complex programs or portfolios
- Director of Digital Transformation: Leadership roles overseeing enterprise initiatives or business unit transformations
- Chief Digital/Transformation Officer: Executive positions leading organization-wide transformation strategy
Common entry routes span multiple disciplines. The Open Group explains enterprise architecture as aligning business and IT to support change and transformation, positioning Enterprise Architects as key contributors and common entrants into digital transformation programs. Scaled Agile defines Product Managers and Product Owners as the roles that define and prioritize work to deliver customer value at enterprise scale, making product management a common pathway into digital transformation leadership.
Program management provides another natural transition. PMI defines program management as coordinating multiple related projects to achieve strategic benefits through how most enterprise transformations are executed, so Program Managers frequently lead digital transformation initiatives.
Change management expertise opens transformation doors. Prosci finds projects with excellent change management are 7x more likely to meet or exceed objectives, underscoring why experienced change practitioners often transition into digital transformation roles to drive adoption.
Cloud and technology specialization creates opportunities. AWS recommends establishing a Cloud Center of Excellence staffed by enterprise architects, finance, security, operations, and product roles to drive cloud-enabled transformation, illustrating common backgrounds feeding into digital transformation initiatives.
Emerging roles reflect market evolution. The Future of Jobs Report 2023 lists Digital Transformation Specialists among fast-growing roles and highlights analytical thinking, tech literacy, and AI/big data as top skills for guidance on upskilling paths for entrants.
Takeaway: Digital transformation careers welcome entry from enterprise architecture, product management, program management, change management, and cloud roles, with progression spanning from analyst positions to C-suite transformation leadership based on demonstrated ability to deliver measurable business outcomes.
Which associations support digital transformation professionals?
Professional associations provide networking, education, and thought leadership that accelerate digital transformation careers. Membership in relevant organizations signals commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
Core transformation and project delivery associations include:
- Project Management Institute (PMI): Leading body for program and portfolio and change delivery standards and certifications that underpin complex digital transformation execution.
- Business Architecture Guild: Nonprofit advancing business architecture practices that link strategy to execution for digital transformation.
Technology governance and digital trust organizations offer frameworks:
- ISACA: Global professional association for digital trust, IT governance, risk, security, and audit through core disciplines enabling enterprise-scale digital transformation.
- The Open Group: Global consortium behind TOGAF and enterprise architecture standards used to design and govern digital operating models.
- Global Association of Enterprise Architects: Professional association for enterprise architects aligning business and technology roadmaps central to transformation.
Process and operations excellence communities provide improvement methods:
- Association of Business Process Management Professionals (ABPMP): Global BPM association focused on process analysis, design, and optimization as key levers in digital transformation.
- APQC: Nonprofit providing process and performance benchmarking to inform transformation initiatives.
Data and analytics associations support data-driven transformation:
- DAMA International: Professional association for data management and governance practices critical to successful digital initiatives.
- EDM Council: Global association for data and analytics management through frameworks like DCAM and CDMC foundational to data-driven transformation.
IT service management communities enable reliable operations:
- itSMF USA: U.S. professional community for IT service management and ITIL practices enabling reliable digital operations.
- TBM Council: Nonprofit professional community advancing Technology Business Management to connect IT spend to value in transformation.
Executive networking organizations provide peer connections:
- Society for Information Management (SIM): U.S. community of CIOs and senior IT leaders focused on business strategy, innovation, and leading digital transformation.
Takeaway: Active participation in associations like PMI, ISACA, The Open Group, and ABPMP provides essential certifications, frameworks, networking opportunities, and thought leadership that distinguish digital transformation professionals.
What events benefit digital transformation careers?
Professional conferences provide learning, networking, and exposure to emerging technologies and practices that advance digital transformation careers. Strategic event selection based on role focus and industry maximizes professional development value.
Enterprise technology platform events showcase innovations:
- AWS re:Invent: Cloud, data, AI/ML, and modern architecture conference shaping large-scale digital transformation on AWS.
- Microsoft Ignite: Enterprise event for AI, cloud, security, and platform modernization driving digital transformation on Microsoft technologies.
- Google Cloud Next: Cloud, data, and generative AI conference focused on transforming business operations and applications on Google Cloud.
- Salesforce Dreamforce: Enterprise innovation event for CRM, data, AI, and end-to-end customer experience transformation.
- SAP Events: Digital core, ERP, supply chain, and data-driven transformation conference for SAP-led enterprises.
Strategy and leadership forums address transformation at scale:
- Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo: Flagship CIO and executive event on digital business strategy, AI, and enterprise-wide transformation.
- MIT CIO Symposium: Executive forum on leading digital enterprises, operating models, and innovation at scale.
Data and analytics conferences enable data-driven transformation:
- Gartner Data & Analytics Summit: Strategy and execution for data, analytics, and AI as core enablers of digital transformation and value realization.
Process and operational excellence events drive improvement:
- OPEX Week: Global forum on operating model reinvention, process excellence, and end-to-end transformation delivery.
- Digital Transformation Week: Cross-industry conference focused on digital strategy, enterprise platforms, automation, and cloud-native innovation.
Industry-specific transformation conferences provide context:
- TMForum’s DTW: Telecom and enterprise leaders gather to re-architect operating models, platforms, and AI-enabled digital transformation.
Takeaway: Regular attendance at conferences like AWS re:Invent, Microsoft Ignite, Gartner IT Symposium, and OPEX Week provides essential exposure to emerging technologies, frameworks, and best practices while building networks that accelerate digital transformation careers.
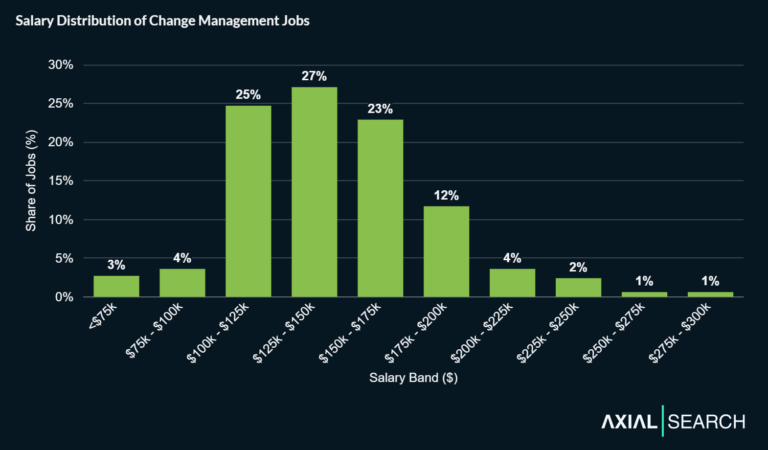
Salaries for digital transformation jobs
Digital transformation compensation reflects the strategic importance and scarcity of experienced practitioners. Salaries vary significantly based on experience level, geographic location, industry, and organizational scope.
Compensation ranges by role level include:
- Digital Transformation Consultant: Median total pay of $233K, with estimated total pay often falling between roughly $175,000 and $320,000 per year in the United States.
- Digital Transformation Project Manager: Estimated total pay typically ranges from about $139,000 to $240,000 per year in the United States, with median total pay of $181K.
- Director, Digital Transformation: Median total pay around $260K, with a range from about $195,000 to $350,000 per year in the United States.
Total compensation extends beyond base salary. Additional pay can include cash bonuses, equity grants, profit sharing, and performance incentives that can increase total earnings by 20-40% above base salary depending on company size and performance.
Geographic factors significantly impact compensation. Major technology hubs like San Francisco, New York, Seattle, and Boston typically offer 20-40% premiums over national averages to reflect cost of living and competitive talent markets.
Industry variations affect pay scales. Technology companies, financial services, and consulting firms generally provide premium compensation compared to healthcare, education, or government sectors. Company size also matters, with large enterprises and high-growth technology companies offering higher total compensation packages.
Takeaway: Digital transformation salaries span from $140K for project manager roles to $350K+ for director positions, with total compensation packages including bonuses and equity that can significantly increase earnings above base salary.
Final thoughts
Digital transformation jobs represent one of the most critical and dynamic career paths in today’s business environment. As organizations face existential pressure to reinvent themselves through technology, AI, and new operating models, skilled practitioners who can bridge strategy and execution will remain in high demand. Whether you’re transitioning from enterprise architecture, program management, or technology roles, the combination of technical depth, strategic thinking, and change leadership makes digital transformation a career that delivers both professional growth and measurable business impact.