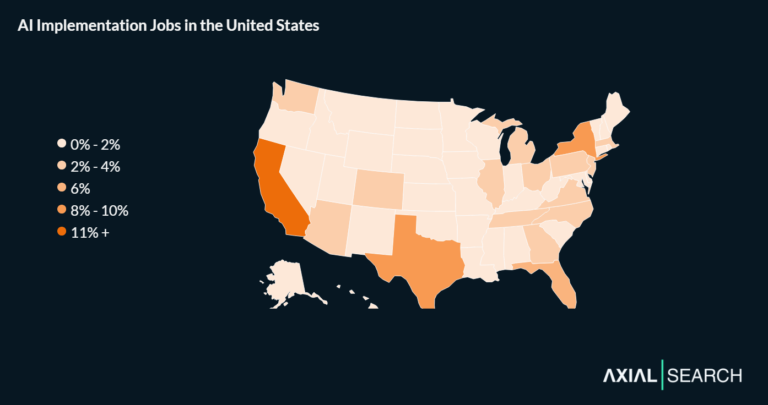
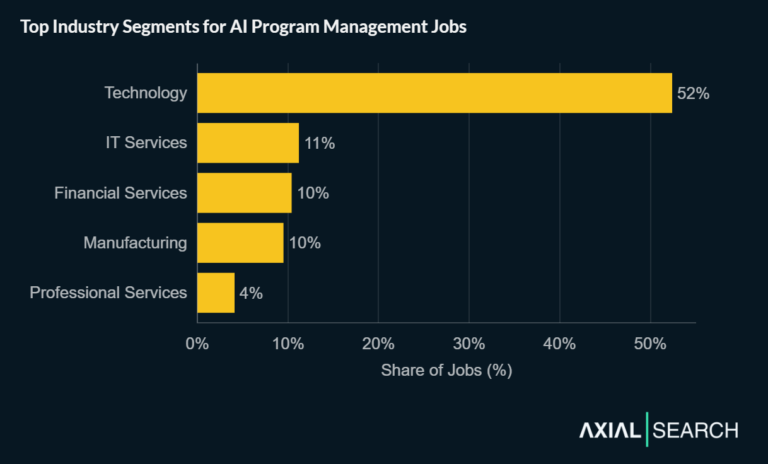
The need for intelligent automation jobs today
Intelligent automation professionals solve a fundamental business challenge: translating AI potential into measurable operational value.
High-value AI programs measure individual-level outcomes like improved decision quality and personal productivity, alongside organizational outcomes such as process efficiency and financial results. This dual focus makes AI automation professionals critical to achieving enterprise goals.
The impact becomes tangible through process improvements. Organizations quantify pre/post automation improvements in process KPIs such as cycle time, touch time, rework rate, conformance, and on-time delivery using process mining analytics. These metrics demonstrate how intelligent automation careers deliver value beyond simple task elimination.
Takeaway: Intelligent automation jobs bridge the gap between AI capability and business outcomes by deploying adaptive systems that measure and improve both individual performance and enterprise-wide process efficiency.
What responsibilities come with intelligent automation jobs?
AI automation jobs span discovery, design, development, deployment, and governance of intelligent systems. The work combines technical depth with business acumen to deliver solutions that handle both structured and unstructured work.
Core responsibilities include:
- Process Discovery: Use process mining to discover how work actually executes, quantify bottlenecks and value potential, and prioritize high-impact candidates for intelligent automation.
- Architecture Design: Design the intelligent automation architecture by integrating components such as process mining, RPA, workflow orchestration, decision management, and AI/ML including NLP and computer vision to handle structured and unstructured work.
- Automation Development: Design, build, and test automations using a development environment to model workflows, integrate applications and AI services, apply reusable components, and debug before deployment.
- Human-in-the-Loop Design: Design human review steps for AI outputs and critical decisions by configuring conditions that trigger human review, routing tasks to reviewers, and capturing outcomes to improve models and processes.
- Platform Operations: Operate the automation platform by provisioning and managing robots, deploying packages, scheduling jobs, handling queues, and monitoring execution, logs, and alerts.
- MLOps Implementation: Implement MLOps practices including version data and models, automate training and deployment with CI/CD, and continuously monitor models for performance and drift to keep intelligent automations reliable.
- AI Governance: Establish and run governance for AI in automation programs by defining risk policies, documenting and managing risks across the AI lifecycle, and applying the NIST AI RMF functions to ensure trustworthy, accountable automation.
- Security and Compliance: Establish bot identity and access controls, segregate duties, manage credentials securely, apply change control, and retain detailed audit logs to meet governance and compliance requirements.
Takeaway: Process automation careers require end-to-end expertise from discovering automation opportunities through process mining to implementing secure, governed AI systems that blend human judgment with machine intelligence.
How are AI automation jobs structured within organizations?
Intelligent automation roles typically sit within centralized or hybrid organizational models designed to scale automation capabilities across the enterprise. Structure varies based on organizational maturity and transformation scope.
Establishing a central Automation Center of Excellence is a common way to organize intelligent automation, consolidating standards, tooling, pipeline management, and delivery to scale across the enterprise. This CoE model provides consistency while enabling business units to pursue local automation opportunities.
Leadership positioning reflects strategic importance. The Federal RPA Playbook calls for a CXO-level executive sponsor such as CFO or COO and a centralized program office or CoE, with CIO engagement. This indicates RPA and IA leaders typically report into senior operations or finance leadership with strong IT partnership.
Team composition combines leadership and execution capabilities. The Playbook outlines roles such as Program Manager or CoE Lead, Solution Architect, Developers, Business Analysts or Process SMEs, and Operations roles. Intelligent automation includes leadership roles with direct reports alongside individual contributors who build and maintain automations.
Takeaway: AI automation jobs are commonly structured within Centers of Excellence reporting to senior operations or finance executives, featuring Program Managers, Architects, Developers, and Business Analysts who collaborate to deliver enterprise-scale automation.
Key skills for intelligent automation careers
Process automation careers demand a distinctive skill blend combining technical automation capabilities, AI literacy, process analysis, and collaborative leadership. These competencies enable practitioners to identify opportunities, architect solutions, and deliver measurable value.
Foundational technical skills include:
- Process Modeling: Ability to model processes with BPMN and automate decisions with DMN is critical for designing and orchestrating complex automations.
- UI Automation: UI element identification and selector design are foundational technical skills; selectors precisely locate on-screen elements and must be robust to changes.
- Document Understanding: Intelligent automation roles require proficiency with document understanding pipelines that combine OCR, ML models, data labeling, and human validation to extract data from unstructured documents.
- Integration Design: API-led connectivity and integration design including REST and event-driven patterns are essential to connect systems and orchestrate end-to-end automations.
- Data Engineering: Building reliable data pipelines including ETL/ELT, ensuring data quality, and preparing datasets are critical to feed AI-enabled automations.
Platform and scale capabilities include:
- Digital Workforce Management: Managing digital workforce at scale through scheduling, monitoring, credentialing, and queue-based workload management is a core IA skill enabled by platforms like Orchestrator.
- Process Mining: Process mining skills using event logs to discover bottlenecks and automation opportunities are key to targeting and scaling Intelligent Automation.
- MLOps: Skills in CI/CD for ML, pipeline automation, model monitoring, and reproducibility are required to operate AI components within Intelligent Automation at scale.
- Hyperautomation Orchestration: Hyperautomation requires orchestrating multiple technologies including RPA, low-code, process mining, and AI, so integration and platform skills are increasingly vital.
Strategic and governance competencies include:
- Human-in-the-Loop Design: Designing human-in-the-loop steps such as approvals and exception reviews is a core IA competency to handle ambiguity and compliance requirements.
- Governance and CoE Practices: Establishing guardrails, environment strategy, and governance including CoE practices is increasingly important as low-code citizen development expands automation footprints.
Interpersonal capabilities round out the skillset. Communication, problem solving, and collaborative leadership are among the most critical power skills linked to better project outcomes and value delivery. The World Economic Forum identifies analytical thinking and creative thinking as the top two core skills for 2023-2027, underpinning problem framing and solution design in Intelligent Automation.
Takeaway: Success in intelligent automation careers requires mastering process modeling, UI automation, and document understanding alongside platform management skills, MLOps capabilities, and strong communication to deliver enterprise-scale solutions.
What frameworks drive success in intelligent automation jobs?
Intelligent automation professionals leverage multiple frameworks to systematically discover opportunities, design solutions, manage risk, and sustain value. Proficiency across these models enables practitioners to select the right approach for each situation.
Process improvement and quality frameworks include:
- DMAIC: Apply Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control to select and improve candidate processes for automation and to stabilize outcomes post-deployment.
- Value Stream Mapping: Map current and future states to expose waste, delays, and handoffs, pinpointing where intelligent automation creates the most flow and customer value.
- Statistical Process Control: Monitor automated processes with control charts to distinguish common versus special cause variation and trigger corrective actions before SLA breaches.
AI and MLOps frameworks include:
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework: Use NIST’s Govern-Map-Measure-Manage functions to systematically identify, assess, and manage AI risks so intelligent automations are valid, reliable, safe, secure, and accountable.
- MLOps Lifecycle: Adopt an MLOps lifecycle with CI/CD for ML, automated pipelines, monitoring for training-serving skew, and continuous retraining to keep AI-driven automations robust in production.
- DORA Metrics: Use the four key metrics including deployment frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and time to restore service to improve automation delivery and reliability.
Governance and value frameworks include:
- COBIT: Use COBIT to align intelligent automation with enterprise objectives, define decision rights, and manage risk, benefits, and performance across stakeholders.
- Benefits Realization Management: Define, plan, and track automation benefits with a lifecycle approach so value including cost, quality, speed, and risk reduction is baselined, realized, and sustained.
- ITIL 4: Leverage ITIL 4’s service value system and practices such as Change Enablement, Incident, Problem, and Release to run AI-enabled automations as reliable services.
Takeaway: Proficiency across process improvement frameworks like DMAIC and Value Stream Mapping, AI governance models like NIST AI RMF, and operational excellence approaches like ITIL 4 enables practitioners to discover, deliver, and sustain intelligent automation value.
Which software tools are vital for AI automation jobs?
Intelligent automation professionals work with diverse software categories spanning RPA platforms, low-code tools, process mining solutions, workflow orchestration systems, and AI services. Mastery of these technologies enables delivery of end-to-end intelligent automation solutions.
Enterprise RPA and intelligent automation platforms include:
- UiPath: Enterprise RPA and AI platform to build, orchestrate, and manage attended/unattended bots with integrated AI/IDP and process mining.
- Automation Anywhere: Cloud-native RPA platform to design, deploy, and scale digital workers with built-in generative AI and governance.
- Pega: AI-powered workflow and decision automation for case management, rules/decisioning, and end-to-end process orchestration.
Workflow and orchestration tools include:
- Camunda: Cloud-native workflow and decision automation using BPMN and DMN to orchestrate humans, services, RPA bots, and microservices.
- Apache Airflow: Open-source platform to author, schedule, and monitor DAG-based workflows for data and automation pipelines.
Integration and connectivity platforms include:
- Boomi: Low-code integration platform to connect cloud/on-prem apps, data, and events that power automated workflows.
Takeaway: AI automation jobs require proficiency across enterprise RPA platforms like UiPath and Automation Anywhere, workflow orchestration tools like Camunda, and integration solutions like Boomi to deliver comprehensive intelligent automation solutions.
Qualifications required for intelligent automation jobs
Intelligent automation roles typically require bachelor’s degrees in computer science, engineering, information systems, or related technical fields. Educational backgrounds provide foundational knowledge in programming, systems thinking, and analytical problem-solving essential for automation work.
Technical degrees align closely with core competencies. Software developers central to intelligent automation delivery typically need a bachelor’s degree in computer and information technology or a related field such as computer science or software engineering. Robotics engineers are classified in Job Zone Four on O*NET, with most occupations requiring a four-year bachelor’s degree commonly in mechanical, electrical, or computer engineering.
Experience often matters as much as formal education. Employers value demonstrated project delivery, problem-solving abilities, and familiarity with process automation technologies. Many successful practitioners build expertise through hands-on implementation work, vendor training programs, and progressive responsibility on automation initiatives.
Cross-functional knowledge is beneficial. Understanding business processes, change management, and stakeholder engagement helps automation professionals identify valuable opportunities and drive adoption. Background in business analysis, process improvement, or operations can complement technical skills.
Continuous learning is essential given the rapid evolution of technology. Professionals stay current through vendor certifications, online courses, industry conferences, and experimentation with emerging tools. The field rewards curiosity and adaptability as AI capabilities and automation platforms advance quickly.
Takeaway: Intelligent automation jobs typically require bachelor’s degrees in computer science, engineering, or related fields, with practical experience and continuous learning through certifications often valued as highly as formal education.
Which certifications benefit intelligent automation careers?
Professional certifications validate expertise in specific platforms, methodologies, and capabilities critical to intelligent automation. Credentials demonstrate commitment to the field and provide structured learning paths for skill development.
Platform-specific RPA certifications include:
- UiPath Advanced RPA Developer: Validates advanced capability to design, build, and deploy complex automations with UiPath including selectors, REFramework, and Orchestrator assets/queues, a core skillset for Intelligent Automation delivery.
- Automation Anywhere Certified Advanced RPA Professional: Demonstrates the ability to build, deploy, and manage bots on Automation 360 including Control Room, error handling, and best practices, widely used in enterprise Intelligent Automation programs.
- Pega Certified Senior System Architect: Validates proficiency in designing and implementing RPA solutions using Pega Robotic Automation including bot deployment and troubleshooting in enterprise environments.
- Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer Associate: Confirms skills to build and orchestrate attended/unattended RPA with Power Automate for desktop and cloud flows and integrate with the Power Platform, key for Microsoft-centric Intelligent Automation.
AI and cloud certifications include:
- Azure AI Engineer Associate: Validates ability to design, build, and integrate AI solutions using Azure AI Services including applied responsible AI, key for Intelligent Automation that blends AI with workflow and RPA.
- Google Cloud Professional Machine Learning Engineer: Confirms capability to design, build, and productionize ML solutions and pipelines on Google Cloud, relevant for IA systems that incorporate ML-driven decision automation.
Process improvement and quality certifications include:
- ASQ Certified Six Sigma Black Belt: Demonstrates mastery of DMAIC, process capability, and improvement methods, highly valued for Intelligent Automation to prioritize, optimize, and measure automation-ready processes.
- ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level – Test Automation Engineering: Certifies competence to design, develop, and maintain test automation solutions and frameworks, essential for assuring reliability and regression safety of automated workflows and bots.
Project and program management certifications include:
- PMP – Project Management Professional: Globally recognized credential validating the ability to lead and deliver projects on time and budget, a strong signal for managing multi-stakeholder Intelligent Automation programs.
Takeaway: Platform certifications like UiPath Advanced RPA Developer and Automation Anywhere Advanced RPA Professional validate core automation skills, while credentials in AI, Six Sigma, and project management demonstrate the broader capabilities required for intelligent automation careers.
Pathways for intelligent automation careers
Intelligent automation offers diverse career trajectories with opportunities to enter from adjacent fields and progress through increasing technical depth or leadership scope. Professionals advance by expanding their technology stack, industry expertise, or organizational influence.
Typical career progression follows this pattern:
- RPA Developer/Automation Developer: Entry-level roles building and testing individual automations
- Senior RPA Developer/Automation Engineer: Mid-level practitioners designing complex solutions and mentoring juniors
- Automation Architect/Solution Architect: Experienced professionals architecting enterprise automation strategies
- Automation Manager/Program Manager: Leaders overseeing automation portfolios and teams
- Director of Automation/Head of CoE: Executives establishing automation strategy and capability
Citizen development creates alternative pathways. PMI defines citizen development as non-IT users creating applications using low-code/no-code tools, enabling business professionals like analysts and process owners to enter intelligent automation by building and scaling automations. Fusion development teams pair citizen developers and business experts with professional developers and IT to build solutions, an increasingly common way professionals transition into intelligent automation roles.
The platform certifications listed below demonstrate the ability of aspiring intelligent automation professionals to design end-to-end business solutions. These tools are often the same as those used by AI automation engineers and other automation experts.
Takeaway: Intelligent automation careers progress from developer roles through architecture and management positions, with entry points available through vendor certifications, citizen development programs, and transitions from related fields like software engineering and business analysis.
Which associations support intelligent automation professionals?
Professional associations provide community, learning resources, and industry connections that accelerate career development in intelligent automation. Membership offers access to research, networking events, and credential programs that distinguish practitioners.
Automation-focused associations include:
- Institute for Robotic Process Automation & AI: Dedicated trade association focused on enterprise robotic process automation and AI, offering community, research, and events directly aligned to intelligent automation roles.
- Association for Advancing Automation (A3): North America’s largest automation trade association spanning robotics, AI, machine vision, motion control, and industrial automation, highly relevant to intelligent automation practitioners.
- International Society of Automation: Global standards and professional community for automation and control systems across industries, key for applying AI to industrial and operational automation.
Process and business transformation associations include:
- Association of Business Process Management Professionals: Global professional association for BPM with bodies of knowledge and certifications that underpin process discovery, optimization, and automation at the core of intelligent automation.
Technical and research societies include:
- IEEE Robotics and Automation Society: IEEE society focused on robotics and automation sciences and engineering, supporting intelligent and autonomous systems development.
- IEEE Computational Intelligence Society: IEEE society advancing neural networks, fuzzy systems, and evolutionary computation, the AI techniques often embedded within intelligent automation solutions.
Takeaway: Active participation in associations like IRPA AI, A3, and ABPMP provides essential networking, professional development, and industry insights that advance intelligent automation careers through community engagement and specialized learning opportunities.
What events help grow an AI automation career?
Industry conferences provide concentrated learning, networking, and exposure to emerging technologies that advance intelligent automation careers. Annual events bring together practitioners, vendors, and thought leaders to share innovations and best practices.
Major vendor and platform events include:
- UiPath FORWARD: UiPath’s flagship annual conference for automation leaders focusing on AI-powered automation, RPA, and enterprise transformation.
- Celosphere: Celonis’ flagship process mining and execution management conference for automation and transformation leaders.
- PegaWorld: Pegasystems’ flagship event focused on AI decisioning, workflow automation, and customer engagement solutions.
- ServiceNow Knowledge: ServiceNow’s global conference on digital workflow automation across IT, employee, and customer service experiences.
- Appian World: Appian’s annual low-code and process automation conference for IT and business leaders driving intelligent automation.
Technology and strategy conferences include:
- Gartner Application Innovation & Business Solutions Summit: Gartner’s conference covering hyperautomation, low-code, integration, and app modernization for enterprise automation leaders.
- Power Platform Conference: Conference for makers and leaders using Power Automate, Power Apps, and Copilot/AI to drive workflow and process automation at scale.
Business transformation and operational excellence events include:
- OPEX Week: Leading operational excellence and business transformation summit with dedicated tracks on intelligent automation and process excellence.
- AIIM Global Summit: Association for Intelligent Information Management’s annual event on intelligent information management, content automation, and process modernization.
Takeaway: Regular attendance at conferences like UiPath FORWARD, Celosphere, and Gartner’s Application Innovation Summit provides essential professional development, vendor insights, and networking opportunities that accelerate intelligent automation careers.
Salary trends for intelligent automation jobs
Compensation for intelligent automation roles reflects the specialized technical skills, business impact, and strong market demand for professionals who can deliver AI-powered automation at scale. Salaries vary based on experience level, geographic location, industry, and organizational scope.
Market data indicates competitive compensation ranges:
- Entry to Mid-Level: Glassdoor shows Intelligent Automation Consultant median total pay typically falls near $152,000 including base plus additional compensation. The compensation range for this role is $117K-$199K.
- Management Level: Glassdoor indicates US total pay for Intelligent Automation Manager often around $131,000-$208,000 including base plus additional. The median total pay is $164K per year.
Total compensation packages typically include base salary, performance bonuses, equity in technology companies, and benefits. Additional compensation components can increase total earnings by 15-25% above base salary depending on role level and company structure.
Geographic factors significantly impact compensation. Major technology hubs including San Francisco, New York, Seattle, and Boston typically offer premium salaries 20-40% above national averages to reflect cost of living and competitive talent markets. Remote positions increasingly offer location-adjusted compensation.
Industry variations affect pay scales. Technology companies, financial services, and consulting firms generally provide higher compensation than manufacturing, healthcare, or government sectors. Enterprise-scale implementations command premium rates compared to departmental automation projects.
Takeaway: Intelligent automation jobs offer competitive compensation with consultant roles typically earning $117K-$199K and management positions reaching $131K-$208K, with total packages including bonuses and equity that can significantly increase overall earnings.
Final thoughts
Intelligent automation jobs sit at the intersection of AI innovation and business transformation. As organizations face mounting pressure to adapt quickly and operate efficiently, professionals who can architect, build, and govern intelligent systems that blend human judgment with machine capabilities will remain in high demand. The field offers clear progression paths, competitive compensation, and the satisfaction of delivering measurable impact across industries. Whether you’re entering from software development, process improvement, or citizen development, intelligent automation careers provide opportunities to shape how work gets done in the AI era.