Why business transformation jobs are crucial
Business transformation roles are now essential to long-term growth. Markets are shifting faster than most organizations can adapt, and legacy models no longer hold up against new technologies and customer expectations. Companies that treat transformation as a one-time initiative fall behind those that make it a continuous discipline. Transformation leaders provide that discipline. They connect strategy, operations, and innovation into a single roadmap for reinvention.
The data is clear. Reinventors—organizations pursuing total enterprise reinvention—achieve roughly twice the revenue growth of their peers. These companies treat transformation as an ongoing capability, not a project with an end date. They rethink how value is created, streamline operations, and embed adaptability across the business. This level of reinvention separates leaders from those who only optimize around the edges.
Transformation professionals make that possible. They align investment, talent, and technology around a clear vision for growth. They help organizations simplify what’s complex, modernize operations, and build resilience for what’s next. With the right transformation leadership, companies can evolve continuously, unlock new sources of advantage, and stay relevant in an unpredictable market. Without it, even strong businesses risk standing still while the market moves on.
Takeaway: Business transformation jobs deliver measurable impact through structured approaches that align strategic initiatives with operational performance, customer outcomes, and shareholder value creation.
What are the main responsibilities in business transformation roles?
Business transformation roles encompass strategic design, operational execution, and organizational enablement across multiple workstreams simultaneously.
Core responsibilities center on systematic change delivery:
- Process Optimization: Apply BPM to identify, design, execute, document, measure, monitor, and control processes; define process owners and KPIs to improve efficiency and outcomes.
- Benefits Realization: Define expected benefits, plan how and when they will be realized, track delivery, and sustain benefits after implementation to capture value from change.
- Executive Sponsorship: Ensure active and visible sponsorship, build a coalition of leaders, and communicate the business reasons for change to maintain momentum and mitigate resistance.
- Change Management: Prepare, equip, and support people through communications, training, coaching, and resistance management so new processes and systems are adopted and sustained.
- Operating Model Design: Redesign structure, processes, people/capabilities, service delivery, technology, data, and governance to translate strategy into day-to-day operations.
- Transformation Office Leadership: Stand up a central office to standardize governance, methods, and reporting; align initiatives to strategy; and track performance across the transformation portfolio.
- Strategic Execution: Translate strategy into objectives, measures, targets, and initiatives; align the organization and monitor outcomes with dashboards to steer the transformation.
- Portfolio Management: Use Lean Portfolio Management to own strategy and investment funding, Agile portfolio operations, and lean governance for the flow of initiatives and value.
Takeaway: Business transformation responsibilities span from strategic design through operational execution, requiring professionals to orchestrate multiple workstreams while maintaining focus on measurable business outcomes.
Where do business transformation roles sit in a company?
Business transformation roles operate at the enterprise level with direct executive oversight and cross-functional authority to drive change across organizational boundaries.
Organizational positioning varies by company structure and transformation scope. A transformation office is commonly led by a chief transformation officer who reports directly to the CEO to give the program top-level authority and visibility. A CEO-sponsored cadence with executive steering committees enables the transformation office to escalate decisions quickly and keep the portfolio on track.
Alternative reporting structures align with functional ownership. Depending on the company, the chief transformation officer and the transformation office may sit under the COO or work closely with the CFO to ensure delivery and value capture.
Critical partnerships define success regardless of reporting structure:
- Technology Leadership: Business transformation professionals coordinate with CIO/CTO and digital strategy teams to sequence technology enablers, modernize platforms, and ensure tech deliverables map to value.
- Operations: Operations leaders are core counterparts to the transformation office to drive throughput, quality, cost, and service improvements across plants, supply chains, and field operations.
- Finance: The transformation office partners closely with Finance to quantify targets, link initiatives to P&L and cash outcomes, and rigorously track benefits realization.
- Human Resources: Transformation leaders work with HR to align incentives, mobilize critical talent, manage workforce transitions, and enable change adoption at scale.
Takeaway: Business transformation roles operate with executive authority and cross-functional partnerships, typically through dedicated transformation offices that coordinate enterprise-wide change initiatives and drive measurable value realization.
Key skills for business transformation jobs
Business transformation careers demand a rare mix of strategic insight, analytical strength and organizational leadership. Successful practitioners align vision, execution and value realization across complex change programs.
Foundational capabilities include:
- Strategic and Analytical Thinking: The World Economic Forum ranks analytical thinking as the top core skill and AI/big data as among the fastest-growing. Transformation leaders need data and AI fluency to guide evidence-based decisions.
- Benefits Realization and Governance: Proven ability to manage benefits, apply mature project practices and deliver on time and on budget is central to effective transformation governance.
Essential technical skills:
- Business Process Management: Model, analyze, measure and improve processes to redesign operations during transformation.
- Change Management: Projects with excellent change management are seven times more likely to meet or exceed objectives, making structured change approaches essential.
- Lean Portfolio Management: Connect strategy to execution through funding, governance and value stream management to prioritize outcomes and manage transformation portfolios.
Critical leadership and interpersonal skills:
- Power Skills: PMI identifies communication, collaborative leadership, problem solving and strategic thinking as decisive for transformation success.
- Influence and Resilience: The World Economic Forum highlights leadership, social influence and agility as key to aligning stakeholders and navigating transformation complexity.
Emerging capabilities:
- Adaptability and Continuous Learning: Eighty-six percent of organizations say adapting to change matters more than ever, but only 18% feel ready—making adaptability a competitive differentiator.
- Technology and AI Literacy: As AI adoption accelerates, transformation leaders must develop GenAI literacy, prompt engineering and governance practices to harness productivity gains responsibly.
Takeaway: Success in business transformation jobs requires mastering analytical thinking, process improvement, and change leadership while developing emerging capabilities in AI literacy, agile delivery, and portfolio management to drive enterprise-wide outcomes.
Which frameworks drive business transformation careers?
Business transformation professionals leverage multiple frameworks to diagnose challenges, design solutions, and execute change at enterprise scale.
Strategic frameworks provide structure for complex transformation initiatives:
- Balanced Scorecard: Translates strategy into objectives, measures, targets, and initiatives across financial, customer, internal process, and learning/growth perspectives; strategy maps depict cause–effect logic for execution.
- Business Model Canvas: A one-page blueprint of the business model across nine building blocks; used to design or pivot value propositions, revenue models, and operating implications during transformation.
- Hoshin Kanri: A strategy deployment method that aligns breakthrough goals with annual priorities through catchball and the X-matrix, closing the strategy–execution gap.
- McKinsey 7-S Model: A holistic lens for aligning Strategy, Structure, Systems, Skills, Staff, Style, and Shared Values; used to diagnose alignment gaps when redesigning operating models.
Operational excellence frameworks drive process transformation:
- DMAIC: A structured improvement cycle—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control—to eliminate waste and variation, commonly used to achieve operational excellence during transformations.
- Value Stream Mapping: A method to visualize end-to-end flow, lead time, information, and waste; pinpoints bottlenecks and informs target-state designs in transformation programs.
- APQC Process Classification Framework: A common taxonomy of cross-industry business processes to benchmark, scope, and redesign processes for target operating models.
Change management frameworks ensure adoption and sustainment:
- ADKAR Model: A people-centered change model (Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, Reinforcement) to drive adoption at scale—critical for realizing benefits in business transformation.
- Kotter’s 8-Step Process: A sequenced approach to mobilize and sustain transformation: create urgency, build a guiding coalition, form a vision, enlist volunteers, remove barriers, generate short-term wins, sustain acceleration, and institute change.
Excellence frameworks provide comprehensive assessment approaches:
- Baldrige Excellence Framework: An integrated management framework to align strategy, customers, operations, workforce, measurement and knowledge, and leadership; used to assess current performance and design transformation roadmaps using the Baldrige Criteria.
Takeaway: Proficiency across strategic, operational, and change frameworks—from Balanced Scorecard and Business Model Canvas to DMAIC and ADKAR—enables transformation professionals to diagnose challenges accurately and design comprehensive enterprise solutions.
What software supports business transformation professionals?
Business transformation professionals leverage diverse technology platforms to plan, execute, and measure complex enterprise initiatives.
Portfolio and strategy execution platforms coordinate transformation initiatives:
- Jira Align: Connects strategy to execution with portfolio roadmaps, dependencies, and OKRs to coordinate agile delivery at enterprise scale.
- Planview: Funds and manages value streams, prioritizes initiatives, and tracks outcomes to align investments with strategy.
- Quantive: OKR software to set objectives, align teams, track KPIs, and run continuous strategy reviews.
Process optimization and automation tools drive operational transformation:
- Celonis: Provides process mining and execution management to discover as-is processes from event data, identify bottlenecks, and prioritize improvements.
- UiPath: Enterprise automation platform for robotic process automation, process orchestration, and AI-powered discovery to digitize manual work at scale.
- Appian: Low-code process automation for BPM, case management, and workflow orchestration to rapidly build and change operational processes.
- Microsoft Power Automate: Low-code workflow automation and robotic process automation across Microsoft 365 and third-party apps via hundreds of connectors.
Data and analytics platforms enable measurement and insights:
- Tableau: Analytics platform to explore data, build interactive dashboards, and share insights that guide transformation decisions.
- Microsoft Power BI: Self-service and enterprise BI for building live dashboards and reports that monitor transformation KPIs.
- Fivetran: Managed ELT pipelines to centralize data from SaaS apps and databases into warehouses for analytics.
Takeaway: Effective business transformation requires proficiency across portfolio management platforms, process optimization tools, and analytics solutions to coordinate enterprise initiatives and measure performance against strategic objectives.
Qualifications for business transformation careers
Business transformation careers welcome professionals from diverse educational and experience backgrounds, with success depending more on demonstrated capability than specific credentials.
Educational requirements typically include bachelor’s degrees in business administration, engineering, finance, operations management, or related analytical fields. Many practitioners hold advanced degrees including MBA, Master’s in Organizational Development, or specialized certifications in process improvement and change management.
Professional experience often outweighs formal education. Employers value demonstrated success leading cross-functional initiatives, managing complex projects, and driving measurable business results. Common entry paths include consulting, finance, operations, IT transformation, and strategy roles.
Industry expertise can provide competitive advantages. Manufacturing and supply chain organizations value Lean Six Sigma experience and operations background. Technology companies seek professionals familiar with agile methodologies, digital transformation, and software delivery. Financial services prioritizes regulatory compliance and risk management experience.
Critical competencies transcend specific backgrounds. Strong analytical skills, data interpretation capabilities, and comfort with financial modeling support evidence-based transformation decisions. Communication and facilitation skills enable stakeholder alignment across organizational levels and functions.
Leadership experience becomes increasingly important for senior roles. Transformation leaders must influence without direct authority, manage competing priorities, and maintain momentum through organizational resistance. Previous experience managing teams, budgets, and complex deliverables demonstrates readiness for transformation responsibility.
Takeaway: Business transformation careers are accessible from multiple professional backgrounds, with success depending on analytical capabilities, leadership experience, and demonstrated ability to drive organizational change and measurable business results.
What certifications are beneficial in business transformation roles?
Professional certifications provide credibility and demonstrate commitment to change management best practices across multiple disciplines.
Project and program management certifications establish foundational governance capabilities:
- Project Management Professional (PMP): Globally recognized credential that validates the ability to lead and direct projects and teams—foundational for governing complex transformation programs.
- PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP): Recognizes knowledge of agile principles, practices, and tools—useful for hybrid and Agile-driven business transformations.
Process improvement and operational excellence certifications drive transformation capability:
- Certified Business Process Professional (CBPP): Certifies BPM knowledge aligned to the ABPMP BPM CBOK—covering process analysis, design, performance, and governance critical to end-to-end process transformation.
- ASQ Six Sigma Black Belt: Demonstrates mastery of Six Sigma philosophies, DMAIC methods, and leadership of improvement projects—core for process transformation and operational excellence.
Architecture and design certifications support operating model transformation:
- Certified Business Architect: Recognizes skills in business architecture grounded in the BIZBOK Guide—capability and value stream mapping to link strategy to execution in transformations.
- TOGAF Certified: Validates knowledge of the TOGAF standard for enterprise architecture—supports alignment of business and IT, capability mapping, and governance in transformations.
Takeaway: Transformation professionals benefit from certifications across project management, process improvement, and enterprise architecture domains, with PMP, CBPP, and Six Sigma Black Belt providing the most directly applicable credentials for business transformation careers.
Career growth in business transformation jobs
Business transformation offers diverse advancement opportunities with multiple entry points and progression paths spanning from analytical roles to enterprise transformation leadership.
Common career progression follows increasing scope and responsibility:
- Business Transformation Analyst: Entry-level roles supporting data analysis, process documentation, and project coordination
- Business Transformation Consultant: Mid-level positions leading workstreams and client initiatives
- Senior Business Transformation Manager: Experienced practitioners managing complex programs and cross-functional teams
- Business Transformation Director: Leadership roles overseeing multiple initiatives and building transformation capability
- Chief Transformation Officer: Executive positions driving enterprise-wide transformation strategy and governance
Entry pathways reflect the cross-functional nature of transformation work. Business transformation professionals commonly originate from finance, operations, or strategy/consulting backgrounds and are often internal leaders elevated to drive cross‑enterprise change. BPM professionals drive enterprise change by aligning processes with strategy, making BPM a common route into Business Transformation leadership.
Specialized backgrounds provide natural transitions. Lean Six Sigma and continuous improvement practitioners often step into Business Transformation roles because they lead cross‑functional process changes that deliver measurable value. Professionals in program and project leadership roles transition into organizational transformation by building strategy execution, benefits realization, and change leadership capabilities.
Transformation offices create career opportunities across multiple disciplines. Enterprise Transformation Offices are staffed with cross‑functional talent with strengths in program/portfolio management, change management, finance/value tracking, and analytics—common feeder roles into Business Transformation.
Takeaway: Business transformation careers offer multiple entry points through related fields like finance, operations, consulting, and process improvement, with clear progression paths from analyst roles to chief transformation officer positions leading enterprise-wide change initiatives.
Which associations support business transformation professionals?
Professional associations provide essential networking, education, and career development resources for business transformation professionals across multiple disciplines.
Core transformation and change management associations include:
- Association of Change Management Professionals (ACMP): Global association for change management practitioners, critical to driving adoption and benefits realization in transformations.
- Project Management Institute (PMI): Global association for project, program, and portfolio management that underpins transformation delivery and governance.
Process and operational excellence organizations offer specialized expertise:
- Association of Business Process Management Professionals (ABPMP): Global professional association for business process management leaders, central to operational and process-led business transformation.
- Business Architecture Guild: Professional association advancing business architecture as a core discipline for enterprise transformation and strategy-to-execution alignment.
Enterprise architecture and technology associations support digital transformation:
- The Open Group: Global consortium for enterprise architecture standards (e.g., TOGAF) foundational to operating model and digital transformation.
Takeaway: Active participation in associations like ACMP, PMI, and ABPMP provides essential networking opportunities, professional development, and industry best practices that distinguish business transformation professionals in the marketplace.
What events advance business transformation director jobs?
Professional conferences provide learning, networking, and exposure to emerging trends that accelerate business transformation careers.
Cross-industry transformation events offer comprehensive coverage:
- BTOES Insights Summit: Large global summit focused on end-to-end business transformation, operational excellence, leadership, culture, and digital change.
- OPEX Week: Flagship cross-industry conference on business transformation, operational excellence, process improvement, lean, automation, and customer-centricity.
- Digital Transformation Week: Cross-industry conference series on enterprise digital transformation, data, AI, cloud, and infrastructure modernization.
Technology and process-focused events provide specialized insights:
- Celosphere: Global process mining and execution management conference showcasing real-world transformation programs and value realization.
- Forrester Technology & Innovation Summit: Analyst-led summit for leaders driving business outcomes through technology, platforms, and operating model change.
Strategic execution and leadership conferences address governance aspects:
- PMI Global Summit: PMI’s flagship event for strategy execution, portfolio delivery, and change leadership that powers enterprise transformations.
Takeaway: Regular participation in conferences like BTOES Insights Summit, OPEX Week, and PMI Global Summit provides essential professional development, networking opportunities, and exposure to emerging transformation practices and technologies.
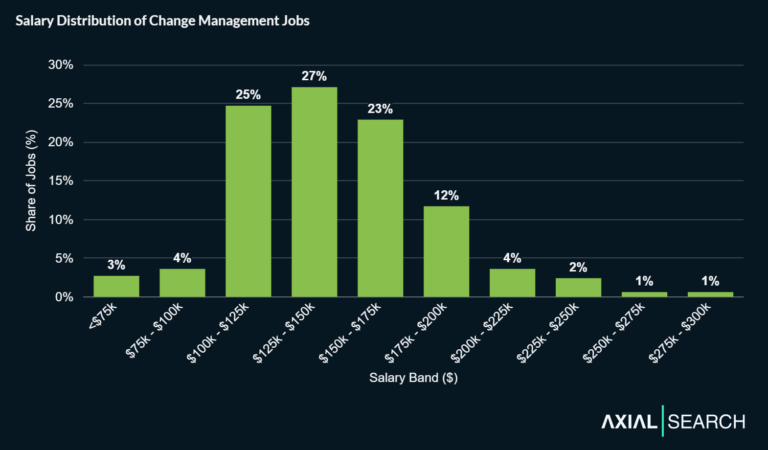
Current salaries for business transformation roles
Business transformation compensation reflects the strategic value and complexity of enterprise transformation leadership, with significant variation based on experience level, industry, and geographic location.
Salary ranges span multiple experience levels:
- Business Transformation Manager: Average annual pay around $170,000; top earners can make $200,000+ reflecting the premium placed on transformation leadership capabilities.
- Business Transformation Consultant: Average annual pay around $167,000, with most salaries falling between approximately $150K and $190,000; top end can reach ~$200K for specialized expertise.
Total compensation packages exceed base salary substantially. Business transformation managers earn median total pay around $186,000 per year, with a most likely range of roughly $140K-$250K (base plus additional pay). Additional compensation typically includes performance bonuses, equity participation, and profit-sharing arrangements that can increase total earnings by 20-40% above base salary.
Geographic factors significantly impact compensation levels. Major metropolitan areas including San Francisco, New York, and Boston typically offer 20-30% premiums over national averages to reflect cost of living. Technology hubs and financial centers generally provide the highest compensation packages.
Industry variations reflect transformation complexity and value. Technology companies, management consulting firms, and financial services typically offer premium compensation compared to government, non-profit, or manufacturing sectors. Companies undergoing major digital transformations often provide competitive packages to attract experienced transformation leaders.
Takeaway: Business transformation salaries range from $140K to $250K+ in total compensation, with significant premiums for experience, location, and industry specialization, reflecting the strategic importance and complexity of enterprise transformation leadership.
Final thoughts
Business transformation jobs represent one of the most dynamic and impactful career paths available in today’s rapidly evolving business environment. As organizations face unprecedented disruption from AI, automation, and market volatility, professionals who can bridge strategy and execution will continue to command premium compensation and advancement opportunities. Whether entering from consulting, operations, finance, or technology backgrounds, transformation careers offer the opportunity to drive measurable enterprise impact while building valuable cross-functional expertise that positions professionals for senior leadership roles.