Key Findings
- Most roles are mid-level: 75% of AI implementation positions target professionals with 5+ years of experience
- Median salary is $162,650: The middle 80% of roles pay between $114K and $231K annually
- Certifications appear in 21% of posts: Microsoft Dynamics 365, PMP and AWS Machine Learning certifications lead requests
- Service firms dominate hiring: Professional Services (46%), Technology (21%) and IT Services (11%) lead postings
- California leads the market: 12% of U.S. roles are posted in California, followed by Texas (10%) and New York (9%)
- Technical degrees preferred: Only 36% of junior roles skip degree requirements, dropping to 31% at senior levels
The Role of an AI Implementation Professional
These patterns align with what we see across AI recruitment, where organizations balance technical execution with strategic transformation.
We categorized each role by seniority and found the market heavily favors mid-level professionals—they account for three-quarters of all postings.
We then extracted experience requirements (86% of roles mentioned a specific number) and calculated the average minimum at each level of seniority. Finally, we analyzed job titles to identify the most common naming conventions at each level.
- Junior (13% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 4 years
- Common titles: AI Adoption Specialist, Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP + AI/Copilot Functional Consultant, AI Automation Engineer
- Mid-Level (75% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 5 years
- Common titles: Manager AI Initiatives and Adoption, AI Strategy Manager, Lead GenAI Engineer
- Senior (12% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 9 years
- Common titles: Director AI Transformation, Head of Data & AI Transformation Programs, Senior Director AI Transformation
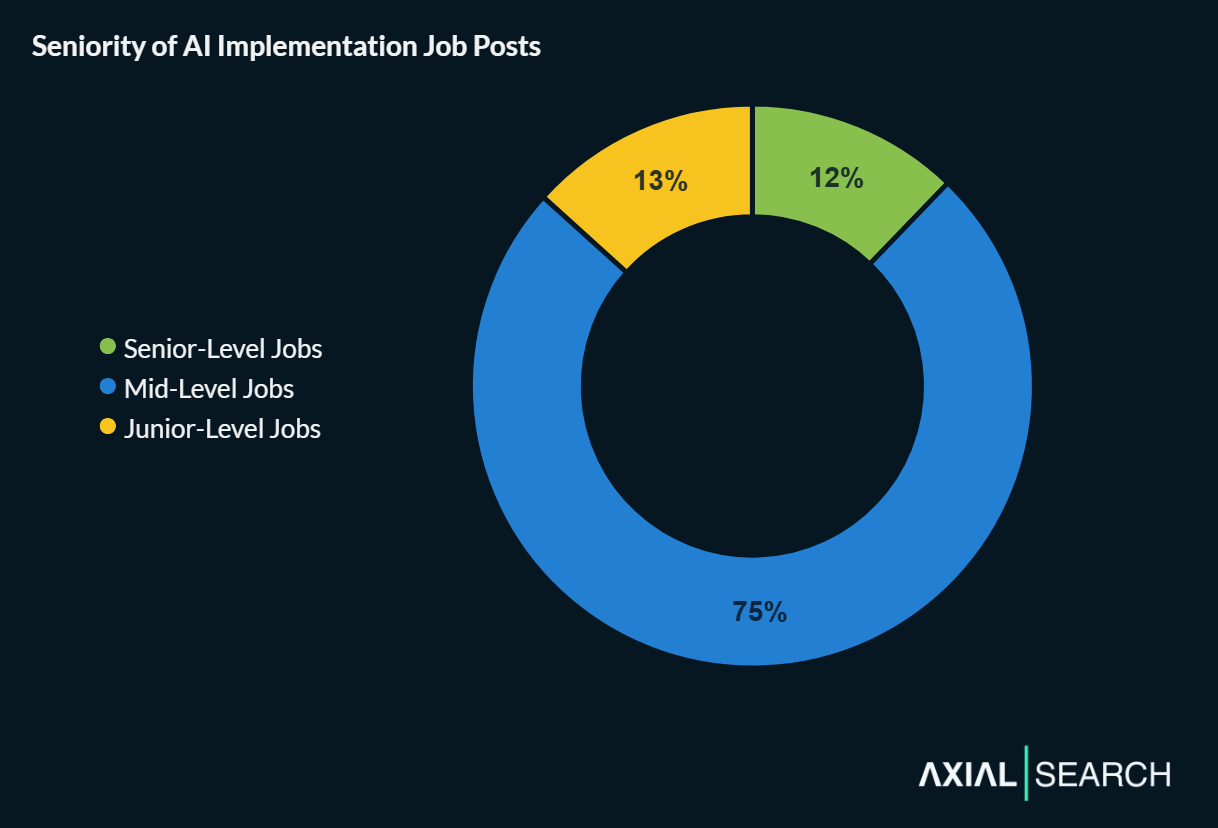
Most AI implementation jobs are mid-level
What Do AI Implementation Jobs Involve?
So what is an AI implementation professional actually responsible for day-to-day? We analyzed the language across all 3,159 job posts to extract the core responsibilities at each level. What emerged is a clear progression of expectations from execution to strategy:
Junior-Level Roles:
- Configure AI-powered automation solutions integrating enterprise platforms
- Translate domain expertise into AI-ready formats through prompt engineering
- Enable end-users through training and consultative solution design
Mid-Level Roles:
- Design enterprise-scale AI systems managing technical teams and stakeholders
- Architect generative AI solutions including RAG pipelines and agent workflows
- Drive adoption strategy by identifying use cases and building proofs-of-concept
Senior-Level Roles:
- Define organizational AI vision and multi-year transformation roadmaps
- Lead presales and delivery of enterprise AI programs across strategy and governance
- Build scalable AI delivery capabilities and operating models
Key takeaway: Junior professionals configure solutions, mid-level leaders architect systems and drive adoption, senior executives define vision and build organizational capabilities. Each step up means more strategic influence over how AI transforms the enterprise.
Who’s Hiring for AI Implementation?
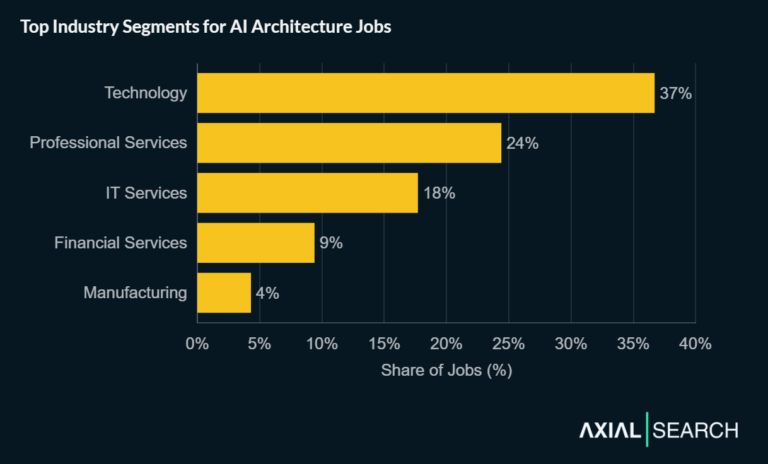
Professional Services firms lead with 46% of AI implementation postings—nearly half the market. This concentration reflects the consultative nature of transformation work, where most professionals either advise enterprise clients through complex implementations or build internal AI systems for tech companies.
Technology companies account for 21%, with IT Services rounding out the top three at 11%. Financial Services (9%) and Manufacturing (3%) complete the top five.
The dominance of service firms makes sense given that AI implementation requires both deep technical expertise and the change management capabilities to drive organizational adoption.
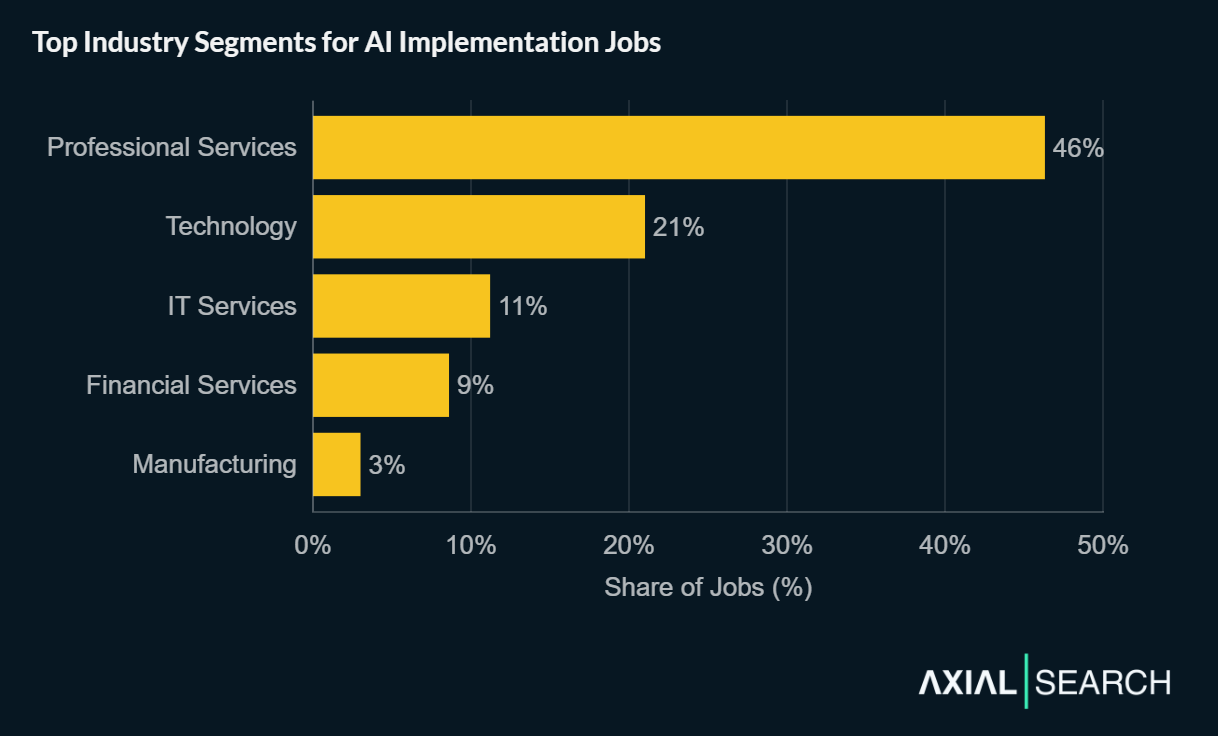
Professional Services firms dominate AI implementation hiring
Large companies with 10,001+ employees account for 55% of postings—well above the economy’s wider workforce distribution of ~30%. Organizations with 1,001-10,000 employees add another 18%, meaning nearly three-quarters of AI implementation roles are at companies with over 1,000 employees.
This concentration suggests AI implementation is still primarily an enterprise-scale function. The complexity of deploying AI across large organizations, combined with budget requirements for transformation initiatives, creates demand that smaller companies rarely match.
That said, small businesses still capture a meaningful share—13% of roles are posted by companies with fewer than 51 employees, suggesting boutique consulting firms create specialized demand.
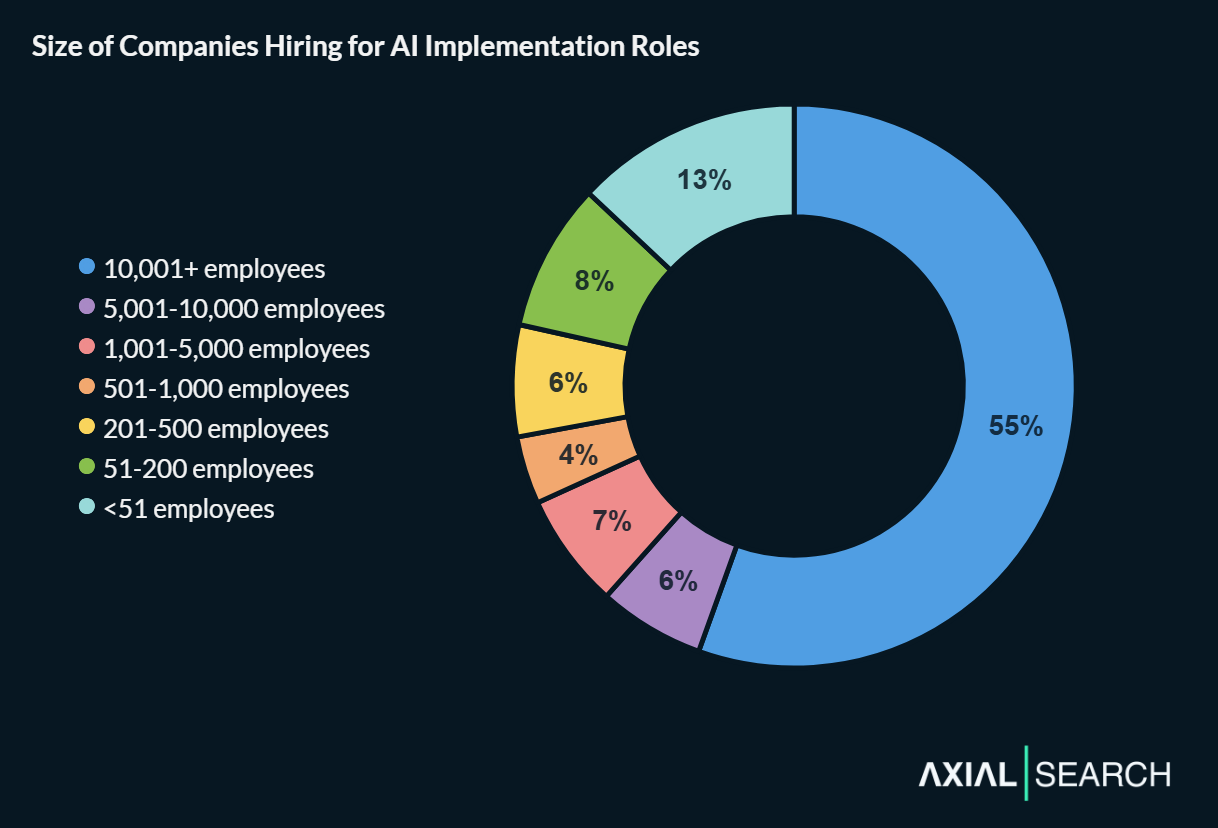
Large enterprises dominate AI implementation hiring
Where Are AI Implementation Jobs Located?
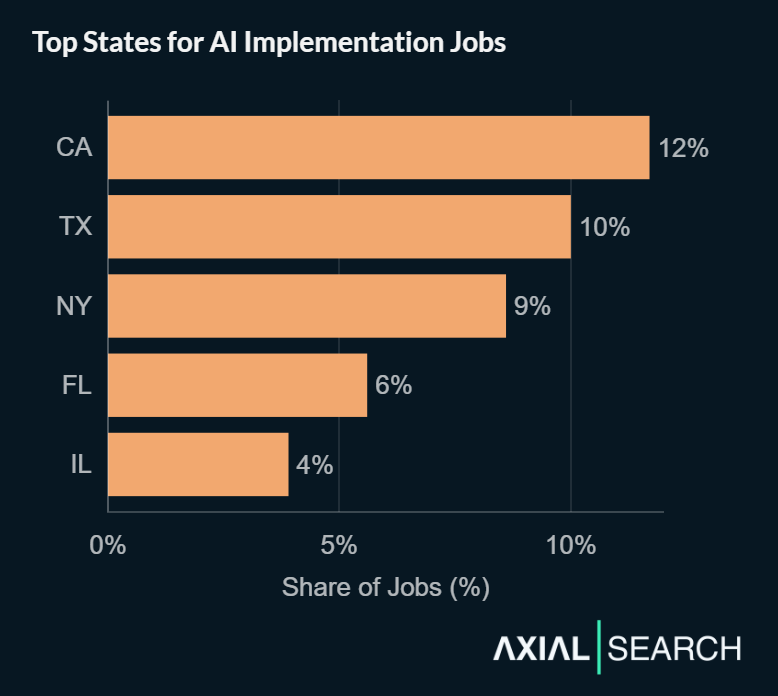
California, Texas and New York lead AI implementation hiring
California leads the market with 12% of all AI implementation postings. Texas follows at 10%, New York at 9%, Florida at 6%, and Illinois rounds out the top five at 4%.
The geographic concentration is less extreme than other AI specializations, though tech hubs still dominate. Remote roles account for just 10% of postings despite the technical nature of the work, suggesting most organizations prefer AI implementation professionals to work on-site where they can collaborate directly with business stakeholders and engineering teams.
States worth watching include Washington, Virginia, Ohio, North Carolina and Georgia—each capturing roughly 3% of the market and representing growing regional tech ecosystems with maturing AI adoption.
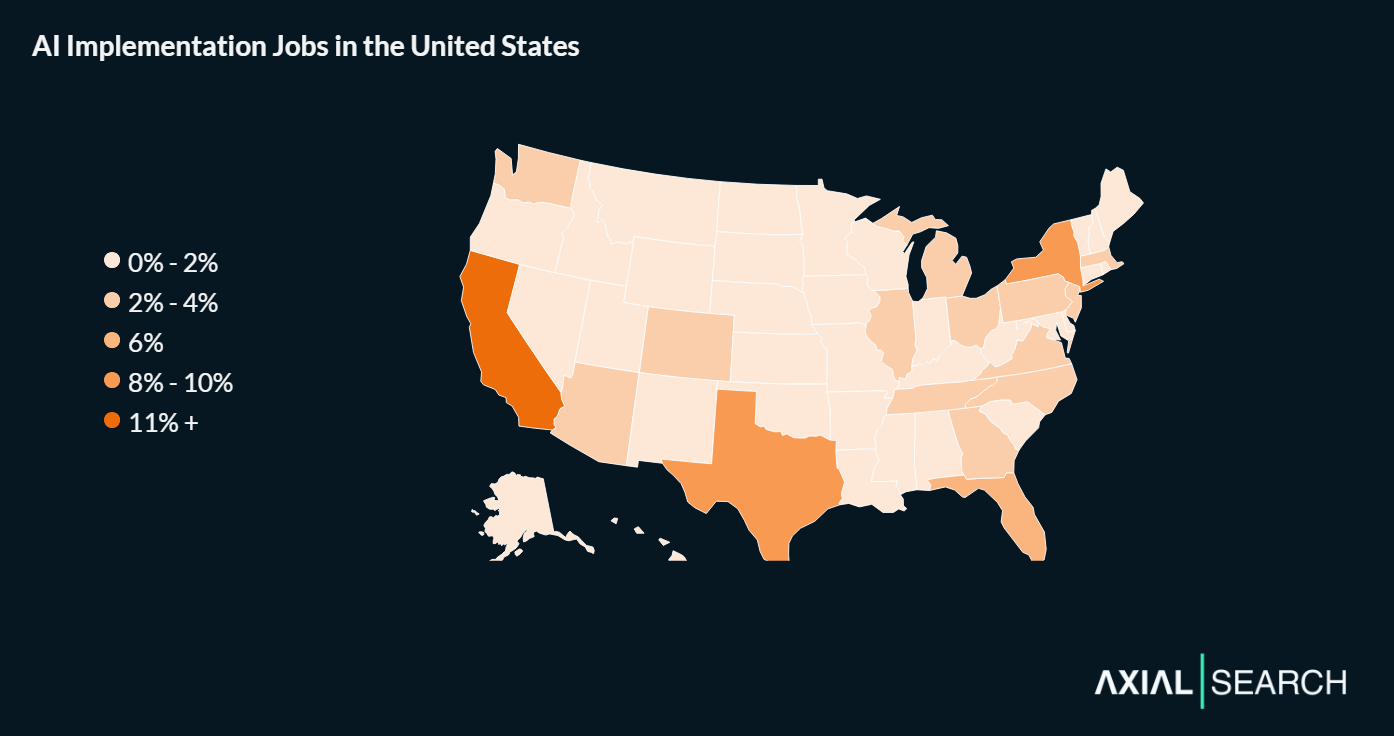
10% of AI implementation jobs offer remote work
Key takeaway: California offers the most AI implementation opportunities by volume, but Texas and New York provide competitive alternatives. The consultative nature of transformation work keeps remote options limited—expect hybrid or on-site requirements for most roles.
Requirements for AI Implementation Jobs
We analyzed the minimum requirements of each job post and found that most AI implementation jobs (70%) require some form of degree. Interestingly, the pattern holds relatively steady across seniority levels—a departure from many technical roles where requirements tighten at senior levels.
For junior roles, 64% require a degree (62% bachelor’s, 2% advanced degrees). The remaining 36% don’t specify formal education requirements.
Mid-level positions show nearly identical patterns: 74% require a degree (68% bachelor’s, 6% advanced degrees).
Senior roles maintain similar requirements: 69% require a degree (65% bachelor’s, 4% advanced degrees).
Degree fields of study that are typically requested of AI implementation professionals include:
- Computer Science (43%)
- Engineering (21%)
- Data Science (15%)
- Business Administration (10%)
- Mathematics (9%)
- Information Systems (8%)
- Business (7%)
- Finance (6%)
- Information Technology (4%)
- Physical Sciences (4%)
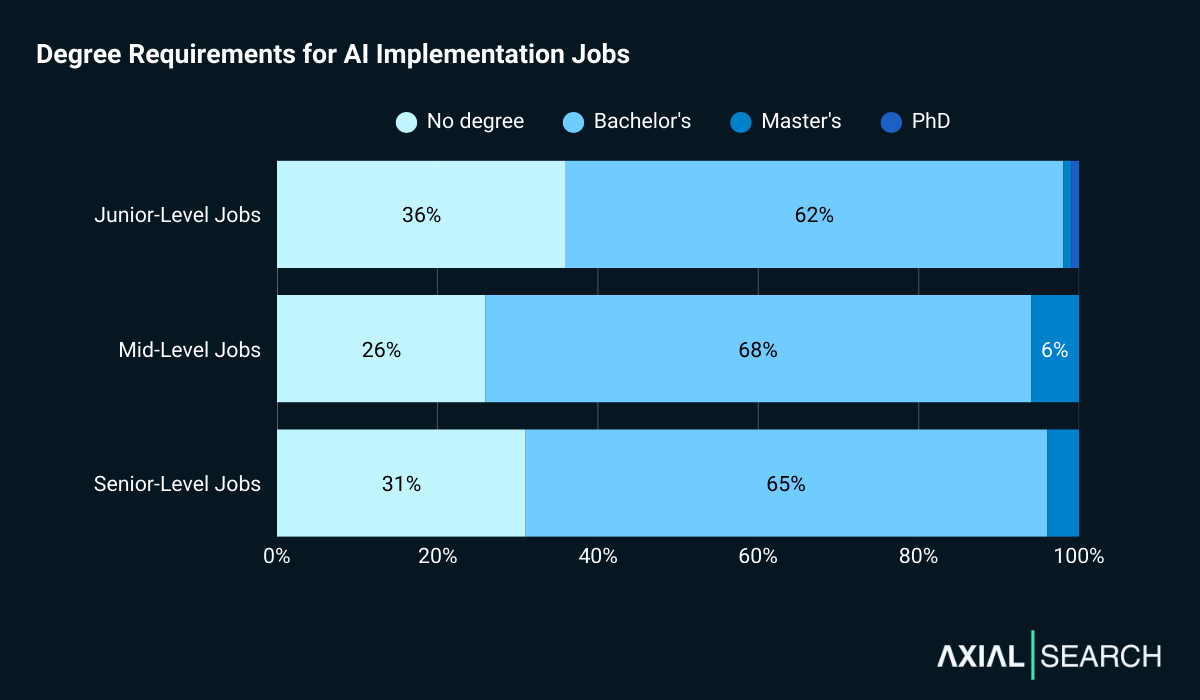
Degree requirements stay consistent across seniority levels
Requested Qualifications in AI Implementation Job Posts
AI implementation professionals must excel at communication, stakeholder engagement and change management. Communication appeared in 30% of listings, stakeholder engagement in 19%, and change management in 18%—reflecting the role’s dual nature as both technical implementer and organizational change agent.
Deep technical expertise matters equally. Machine learning (23% of posts), generative AI (18%) and prompt engineering (12%) are table stakes, supported by hands-on experience with frameworks like Agile, RAG and MLOps.
Just 21% of postings request specific certifications, but when they do, these credentials lead:
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Certification
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- AWS Certified Machine Learning
- Google Cloud Professional ML Engineer
- Artificial Intelligence Governance Professional (AIGP)
- Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP)
- Databricks Certification
- AWS Solutions Architect
Key takeaway: Technical depth matters, but transformation & change management skills like communication and stakeholder engagement separate strong candidates from merely technical ones. Certifications signal platform competence, yet organizational change capabilities drive successful implementations.
What do AI Implementation Jobs Pay?
More than two-thirds (68%) of the AI implementation roles we analyzed included an advertised salary.
There was significant breadth in the ranges employers posted, so we normalized the data by selecting the midpoint for our analysis. From our experience, this is generally a much more indicative number for an employer’s target offer—especially in the current market where initial ranges often run wide.
Across the entire dataset of salaries, we found the median salary for AI implementation positions to be $162,650. The middle 80% of salaries (10th to 90th percentile) ranged from $114,200 to $231,250.
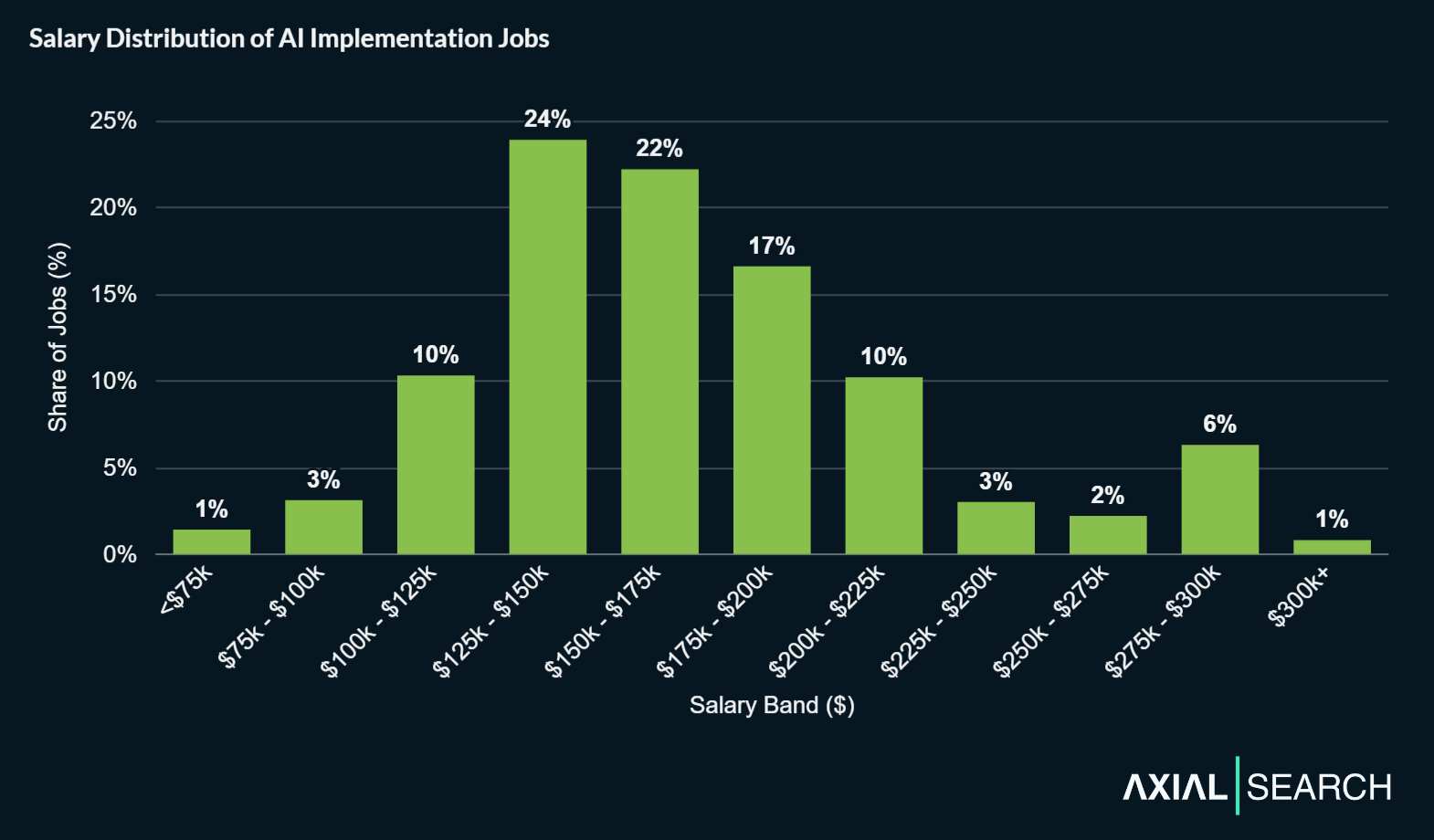
Most AI implementation salaries fall between $114k and $231k
Breaking AI implementation salaries down by seniority reveals modest progression between junior and mid-level roles, with a significant premium at senior levels. Junior roles start at a median $139,500, with mid-level positions climbing just 15% to $160,700. The real jump appears at senior levels—a 28% leap to $205,600 median.
What’s notable is the compression: junior salaries vary by $120,000 from bottom to top ($75K-$195K), mid-level by $93,000 ($114K-$207K), but senior roles cluster within a $122,500 band ($160K-$282K) despite commanding higher absolute numbers.
The overlap between junior and mid-level ranges is substantial—suggesting that specialization and performance matter more than title alone at these career stages. By contrast, senior roles show clear separation, with the 10th percentile senior salary ($160,000) matching the median mid-level position exactly.
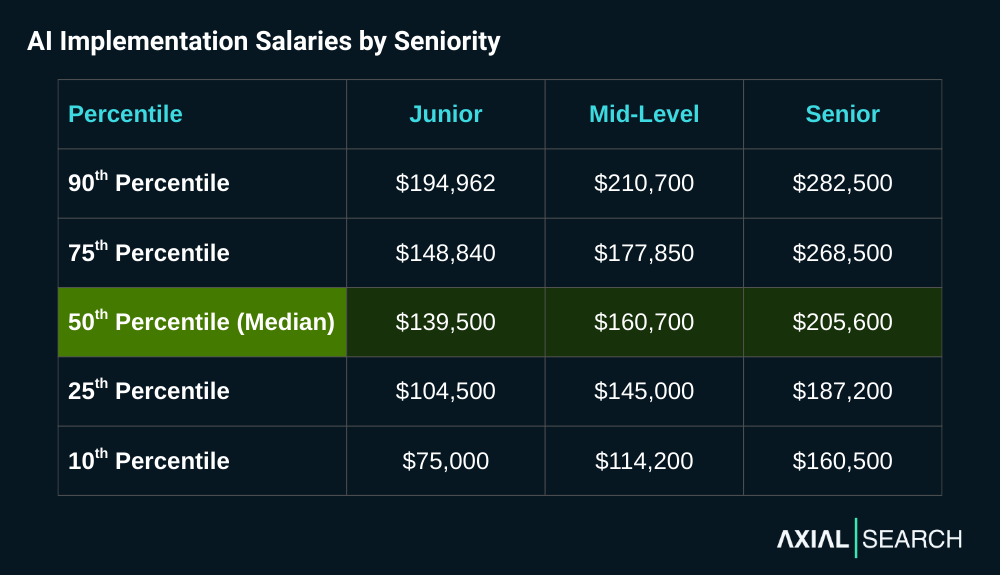
Senior AI implementation professionals are in the top 6% of U.S. earners
Key takeaway: AI implementation positions pay exceptionally well. The median senior-level salary of $205,600 puts these roles in the top 6% of all earners in the United States. Even junior professionals earning the median $139,500 land in the top 13%.
Final Thoughts
For Candidates: Build hands-on experience with generative AI tools and prompt engineering early—these capabilities appear across all levels. For mid-level roles, demonstrating you’ve architected RAG pipelines or agent workflows separates candidates. At senior levels, experience defining transformation roadmaps and building delivery capabilities matters more than technical depth alone. PMP and cloud platform certifications accelerate credibility.
For Employers: The tight salary clustering around $160,700 for mid-level roles reflects market maturity—fall significantly below that and expect longer time-to-fill. The strongest signal for senior candidates is experience leading enterprise transformation programs and building organizational AI capabilities, not just implementing individual solutions. Remote flexibility remains limited despite technical work—expect candidates to push for hybrid arrangements.
Methodology
We analyzed 3,159 AI implementation job postings collected from LinkedIn, Indeed and Glassdoor between November 2024 and January 2025. The dataset was limited to full-time roles posted in the United States that explicitly mentioned “AI implementation,” “AI adoption,” “AI transformation” or close variations in the job title.
Duplicate postings were removed using job title, company name and location matching. Seniority levels were determined by analyzing job titles alongside minimum experience requirements stated in each posting. When experience ranges were provided, the lower bound was used for consistency.
Salary data was extracted from the 68% of postings that included compensation ranges. We used the midpoint of each range for analysis, as this most closely reflects employer target offers in practice.
Industry classifications were assigned based on company descriptions and verified against LinkedIn company data where available. Geographic analysis was conducted at the state level using the primary job location listed in each posting.