Key Findings
- Most roles are mid-level: 75% of change management positions target professionals with 6+ years of experience
- Median salary is $141,534: The middle 80% of roles pay between $105K and $189K annually
- Certifications matter: 52% of postings request credentials such as Prosci, PMP or CCMP
- Service firms dominate hiring: IT Services (23%), Professional Services (18%) and Financial Services (16%) lead postings
- Texas leads the market: 17% of U.S. roles are posted in Texas, followed by New York (12%) and California (11%)
- Degrees increasingly required: Only 32% of roles do not require a degree, with requirements tightening sharply at senior levels
The Role of a Change Manager
This analysis sits within a broader view of how organizations hire for large-scale transformation, shaped by evolving expectations in transformation and change management recruitment.
We categorized each role by seniority and found the market heavily favors mid-level professionals—they account for three-quarters of all postings.
We then extracted experience requirements (85% of roles mentioned a specific number) and calculated the average minimum at each level of seniority. Finally, we analyzed job titles to identify the most common naming conventions at each level.
- Junior (14% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 3 years
- Common titles: Change Manager, Change Management Specialist, Change Management Analyst
- Mid-Level (75% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 6 years
- Common titles: Organizational Change Manager, OCM Lead, Sr. OCM Consultant
- Senior (11% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 10 years
- Common titles: Director of Change Management, Head of Strategic Initiatives & Change Management
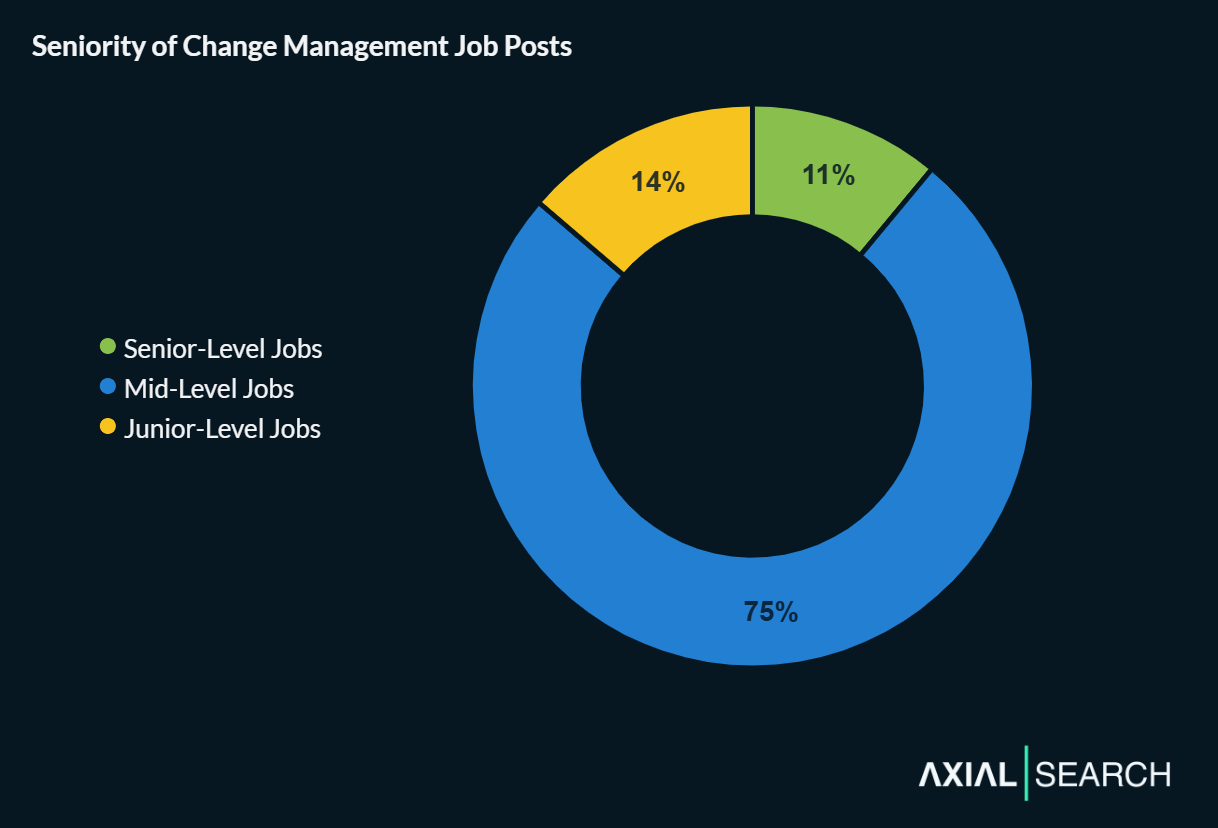
Most change management jobs are mid-level
What Do Change Management Jobs Involve?
So what is a change manager actually responsible for day-to-day? We analyzed the language across all 736 job posts to extract the core responsibilities at each level. What emerged is a clear progression of expectations from tactical to strategic:
Junior-Level Roles:
- Develop communications and training materials for transformation initiatives
- Support stakeholder engagement and adoption tracking
- Execute change activities within defined workstreams
Mid-Level Roles:
- Build change management strategies for process and technology transformations
- Lead cross-functional OCM initiatives end-to-end
- Own stakeholder relationships and resistance management
Senior-Level Roles:
- Design enterprise-wide change frameworks and operating models
- Set strategy for AI, automation, and digital transformation adoption
- Integrate change management with culture and leadership development
Key takeaway: Senior executives shape the framework, mid-level leaders own the strategy, junior employees execute the plan. Each step up means less tactical work and more strategic ownership.
Who’s Hiring for Change Management?
External consultants are often relied upon to lead change management when organizations attempt a major overhaul. So it’s fairly unsurprising that the majority of change management jobs are advertised by third-party service firms.
IT Services leads with 23% of postings, followed by Professional Services (18%) and Financial Services (16%). Technology companies account for 12%, with Construction rounding out the top five at 11%.
Many of these tech and construction firms offer change management services to their own customers, further indicating the often external nature of the role.
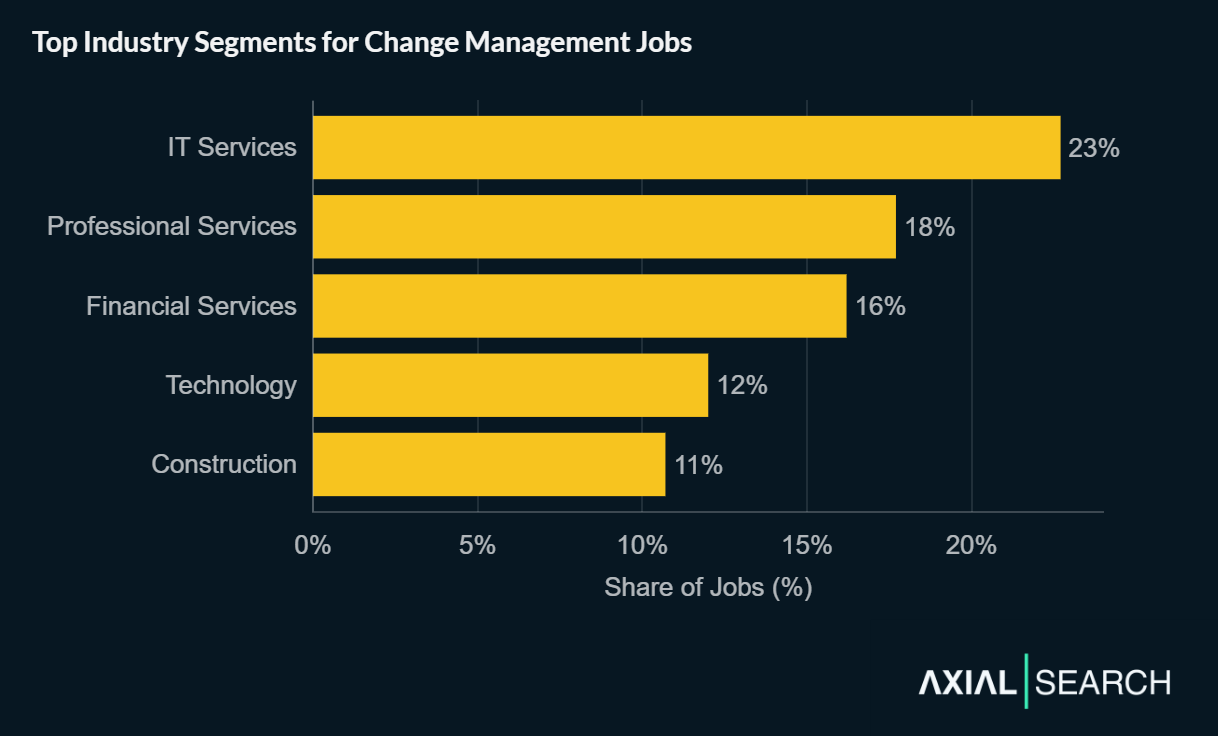
Change management jobs are mostly posted by third-party service firms
Company size follows a predictable pattern. 33% of jobs are posted by enterprises with 10,001+ employees, which is roughly inline with the economy’s wider workforce distribution.
The majority of change management jobs (57%) are posted by “large” organizations with more than 1,000 employees—specifically,
But small and medium-sized businesses still capture a significant share of the market: roughly one-sixth of roles (16%) are advertised by companies with fewer than 51 employees.
This suggests strong demand from boutique consulting firms and growing organizations building out their transformation capabilities.
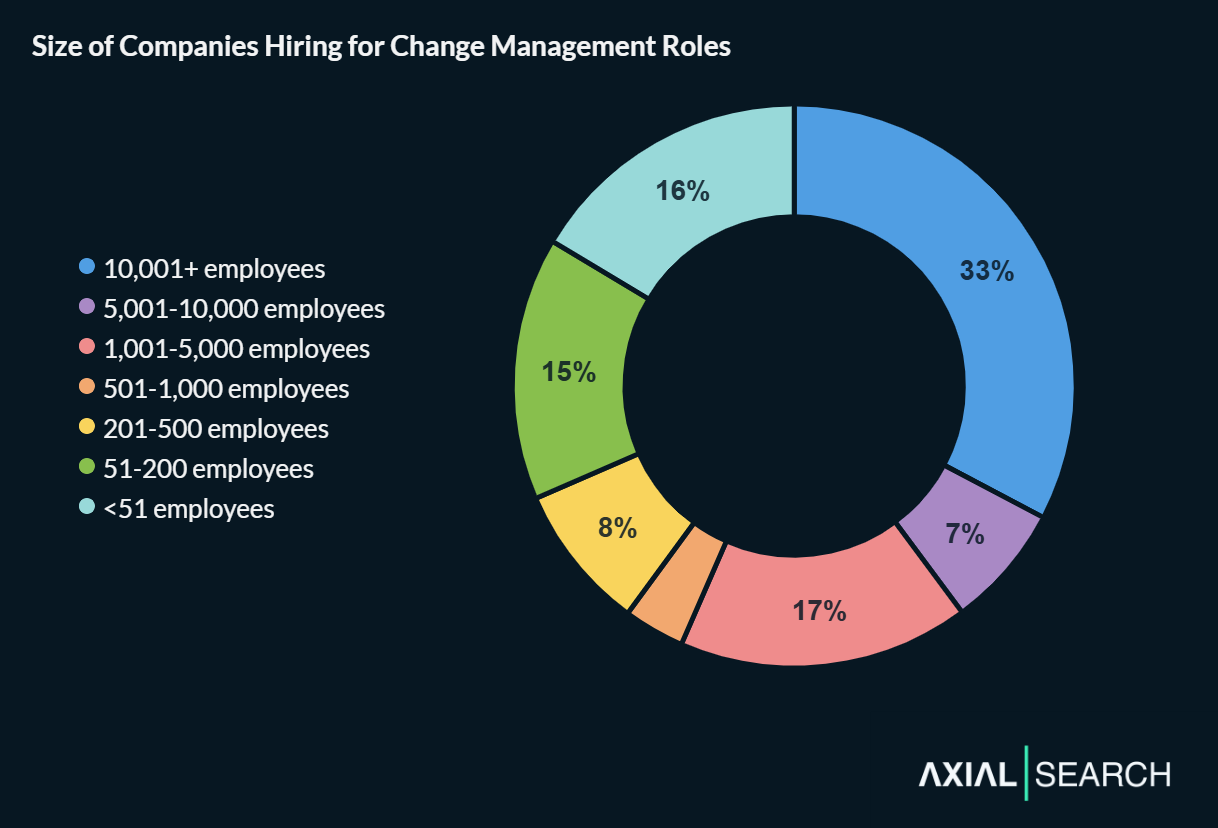
Large companies dominate the change management job market
Where Are Change Management Jobs Located?
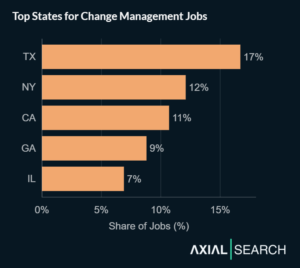
Texas, New York and California lead change management hiring
California, Texas and New York consistently lead U.S. states in GDP output, so it’s no shock to see them top the leaderboard for change management job posts.
But Texas takes the crown here, capturing 17% of all change management postings. New York follows at 12%, California at 11%, Georgia at 9%, and Illinois rounds out the top five at 7%.
The distribution thins out significantly after that, with most roles concentrated along the East and West coasts.
States deserving a notable mention include Washington, Virginia, Florida and North Carolina–each capturing roughly 4% of the change manager job market.
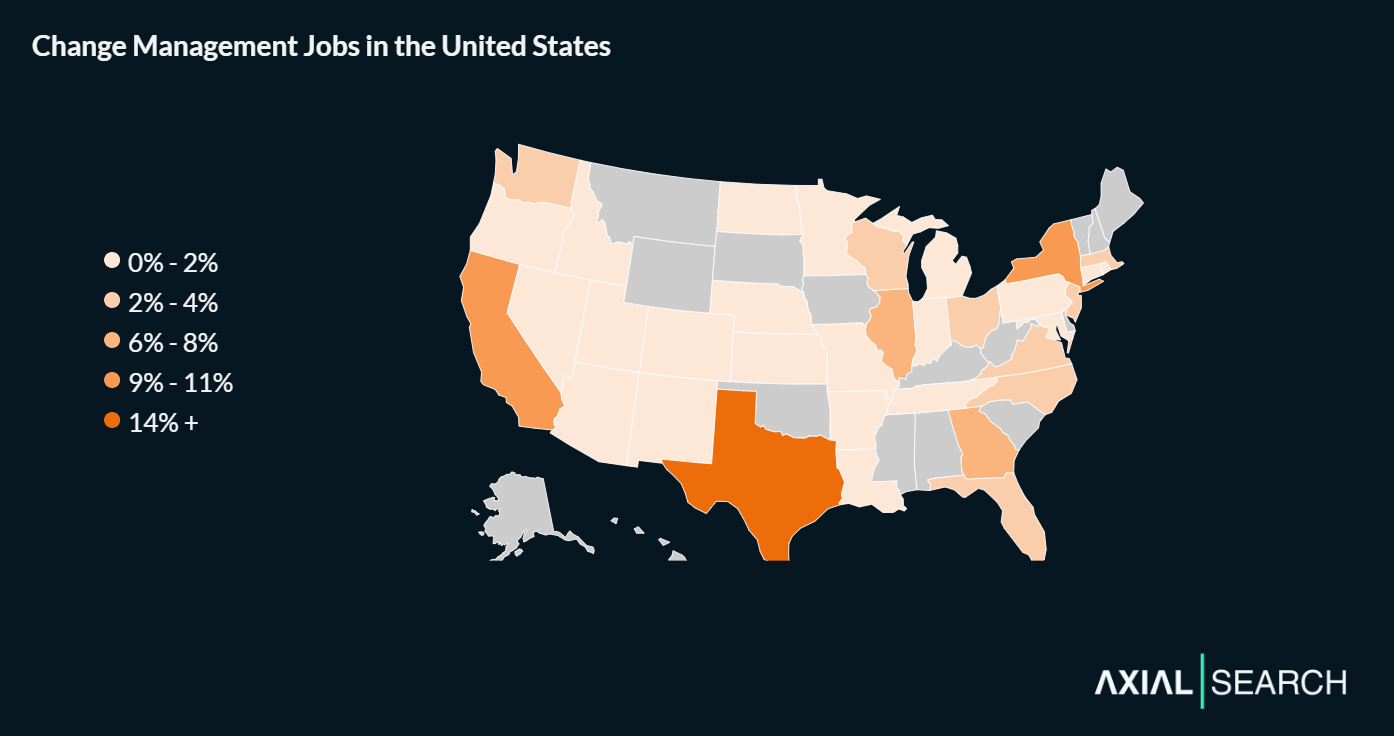
72% of change management jobs are located in 9 states
Key takeaway: If you’re looking for a change management role, Texas offers the most opportunities by volume. But don’t sleep on Georgia—Atlanta’s growing corporate presence is punching above its weight in our dataset.
Requirements for Change Management Jobs
We analyzed the minimum requirements of each job post and found that most change management jobs (68%) require some form of degree. But the story changes significantly by seniority level.
For junior roles, the split is nearly even: 47% require no degree, while 53% ask for a bachelor’s. No junior positions in our dataset required a master’s degree.
Mid-level positions tighten up considerably: 64% require a bachelor’s and 5% specify a master’s degree.
Senior roles have the strictest requirements: 75% require a bachelor’s degree and 9% require a master’s degree.
Degree fields of study that are typically requested of change managers include:
- Business/Business Administration (32%)
- Organizational Development (18%)
- Communications (11%)
- Human Resources (6%)
- Engineering (5%)
- Psychology (4%)
- Information Technology (4%)
- Finance (4%)
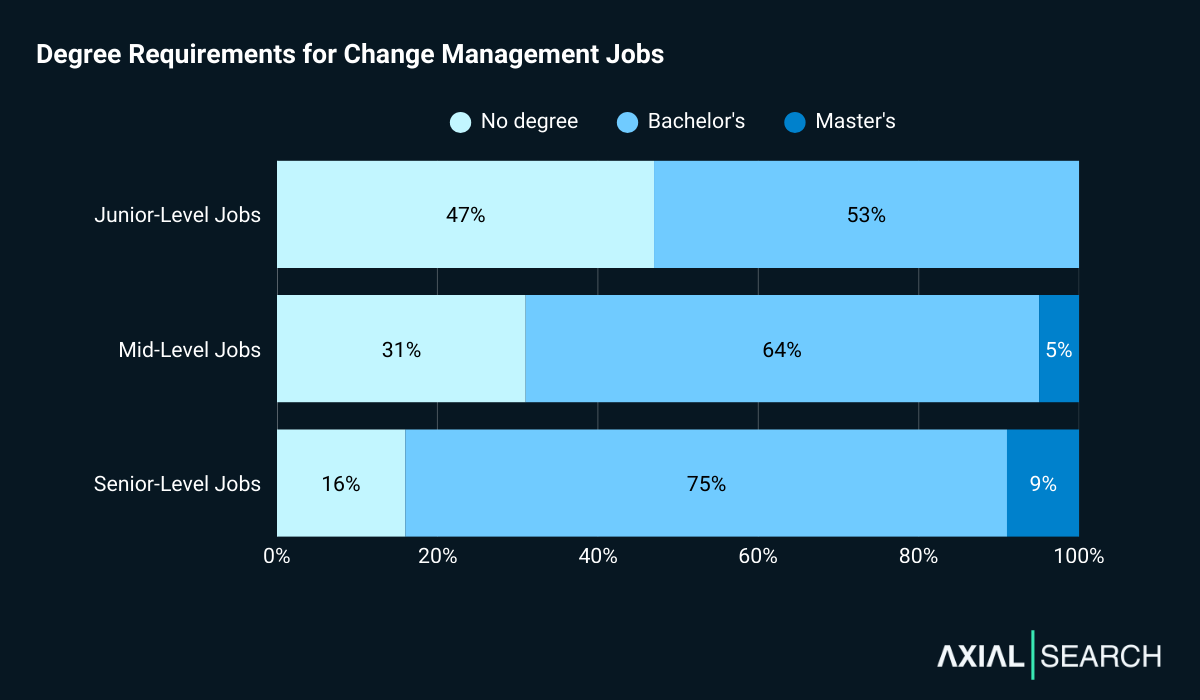
Degree requirements increase as your change management career progresses
Requested Qualifications in Change Management Job Posts
Change management professionals must excel at stakeholder engagement, communication and project management.
These skills directly support the application of structured methodologies that were mentioned throughout the dataset, including ADKAR, Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model, Agile, and Lean Six Sigma.
Certain certifications demonstrate that candidates possess the capabilities required to do the job. Employers are asking for at least one of the following credentials in 52% of job posts:
- Prosci Change Management Certification
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- Certified Change Management Professional (CCMP)
- PRINCE2 Certification
- Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP)
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
- PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)
- ITIL Foundation Certification
Key takeaway: Education and credentials matter in this field. While nearly half of junior roles don’t require a degree, that window closes quickly—and certifications like Prosci and PMP are table stakes for serious candidates at any level.
What do Change Management Jobs Pay?
Just under half (45%) of the change management roles we analyzed included an advertised salary.
There was significant breadth in the ranges employers posted, so we normalized the data by selecting the midpoint for our analysis. From our experience, this is generally a much more indicative number for an employer’s target offer—especially in the current market where initial ranges often run wide.
Across the entire dataset of salaries, we found the median salary for change management positions to be $141,534. The middle 80% of salaries (10th to 90th percentile) ranged from $105,000 to $189,194.
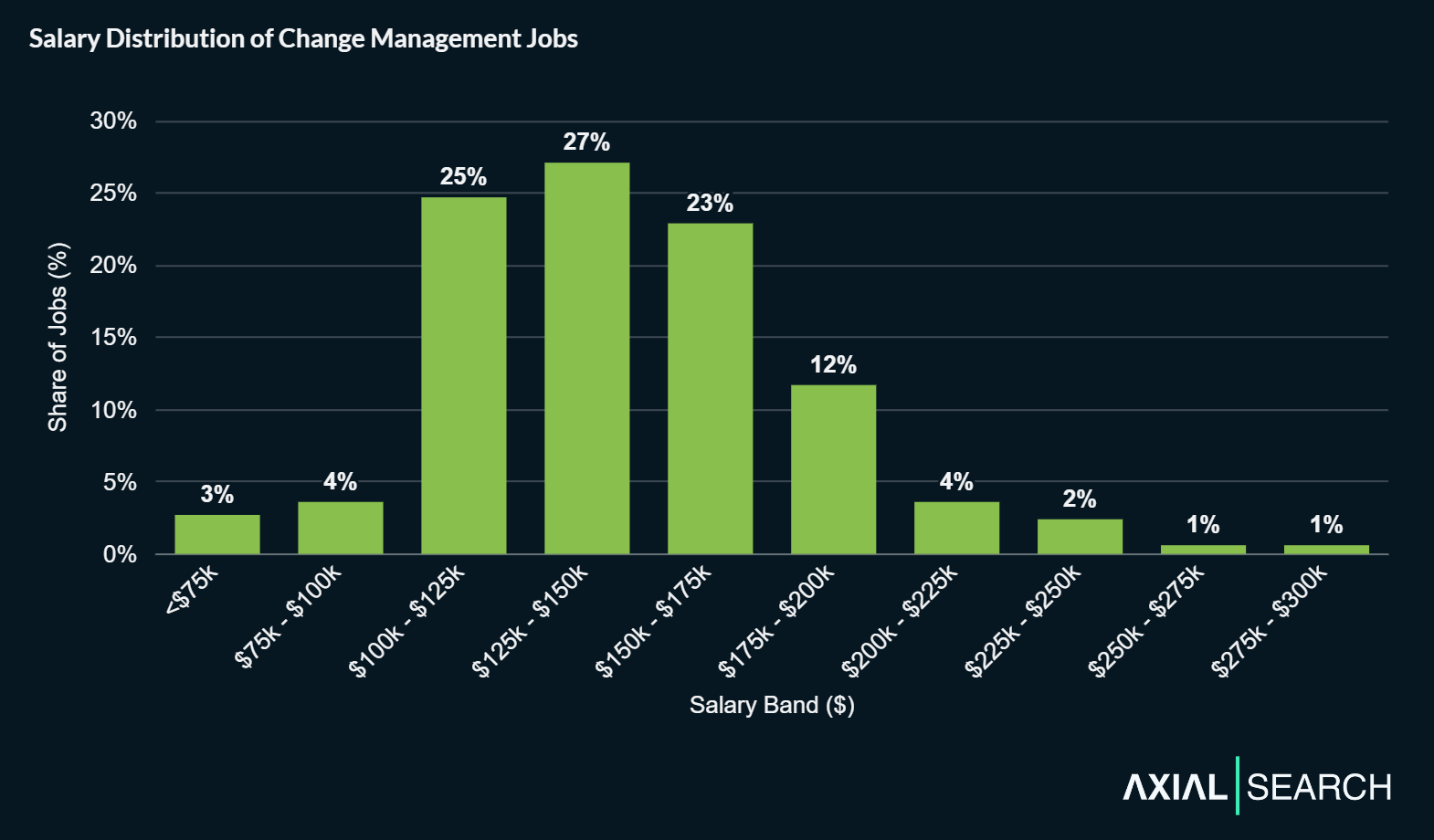
Most change management salaries fall within $105k to $190k
Breaking change management salaries down by seniority reveals an expected progression. The jump from junior to mid-level represents a 24% increase in median salary. The leap to senior adds another 32% on top of that.
What’s notable is the floor at each level: a 10th percentile senior role ($153,235) still out-earns the median mid-level position.
The ranges also tighten as you move up—junior salaries vary by $90,000 from bottom to top, while senior roles cluster within a $72,000 band. This compression reflects market maturity—senior change managers with process optimization expertise command premium positioning within these ranges.
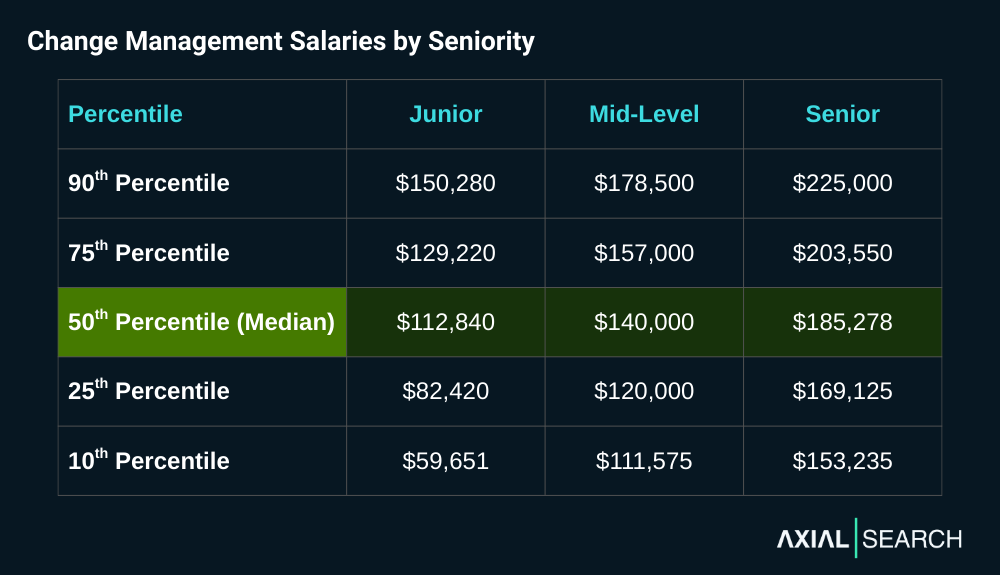
Senior change managers are in the top 7% of U.S. earners
Key takeaway: Change management positions pay well. The median senior-level salary of $185,278 puts these roles in the top 7% of all earners in the United States.
Final Thoughts
For Candidates: Pursue certification early and focus on execution at the junior level. At mid-level, shift toward owning strategy end-to-end—PMP/Prosci credentials pay dividends here. For senior roles, experience with AI and automation adoption is increasingly what separates candidates.
For Employers: Compensation clusters tightly around $140,000 for mid-level roles—fall significantly below that and expect longer time-to-fill. The strongest signal for senior candidates is framework design experience for digital transformation, not just years in the seat.
Methodology
We analyzed 736 change management job postings collected from LinkedIn, Indeed and Glassdoor between November 2024 and January 2025. The dataset was limited to full-time roles posted in the United States that explicitly mentioned “change management” or close variations in the job title.
Duplicate postings were removed using job title, company name and location matching. Seniority levels were determined by analyzing job titles alongside minimum experience requirements stated in each posting. When experience ranges were provided, the lower bound was used for consistency.
Salary data was extracted from the 45% of postings that included compensation ranges. We used the midpoint of each range for analysis, as this most closely reflects employer target offers in practice.
Industry classifications were assigned based on company descriptions and verified against LinkedIn company data where available. Geographic analysis was conducted at the state level using the primary job location listed, including specified states and fully remote roles.