Key Findings
- Most roles are mid-level: 55% of digital strategy positions target professionals with 6+ years of experience
- Median salary is $139,500: The middle 80% of roles pay between $75K and $197K annually
- Certifications rarely appear: Just 7% of postings request credentials, with Google Analytics, CSPO and PMP leading
- Service and media firms dominate hiring: Professional Services (23%), Telecom & Media (22%) and Financial Services (15%) lead postings
- New York leads the market: 12% of U.S. roles are posted in New York, followed by California (9%) and Illinois (7%)
- Degrees increasingly required: Only 32% of junior roles skip degree requirements, dropping to 44% at senior levels
The Role of a Digital Strategy Professional
This analysis sits within a broader view of how organizations hire for large-scale transformation, shaped by evolving expectations in transformation and change management recruitment.
We categorized each role by seniority and found the market heavily favors mid-level professionals – they account for more than half of all postings.
We then extracted experience requirements (85% of roles mentioned a specific number) and calculated the average minimum at each level of seniority. Finally, we analyzed job titles to identify the most common naming conventions at each level.
- Junior (23% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 3 years
- Common titles: Digital & AI Strategy Senior Associate, Digital Marketing Strategist, Digital Health Strategist
- Mid-Level (55% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 6 years
- Common titles: Digital & AI Strategy Manager, Staff Product Manager Digital Strategy, Associate Director Strategy & Insights
- Senior (22% of roles)
- Minimum experience: 8 years
- Common titles: Director Digital Strategy, Chief Digital Officer, Vice President Digital Assets Product Strategist
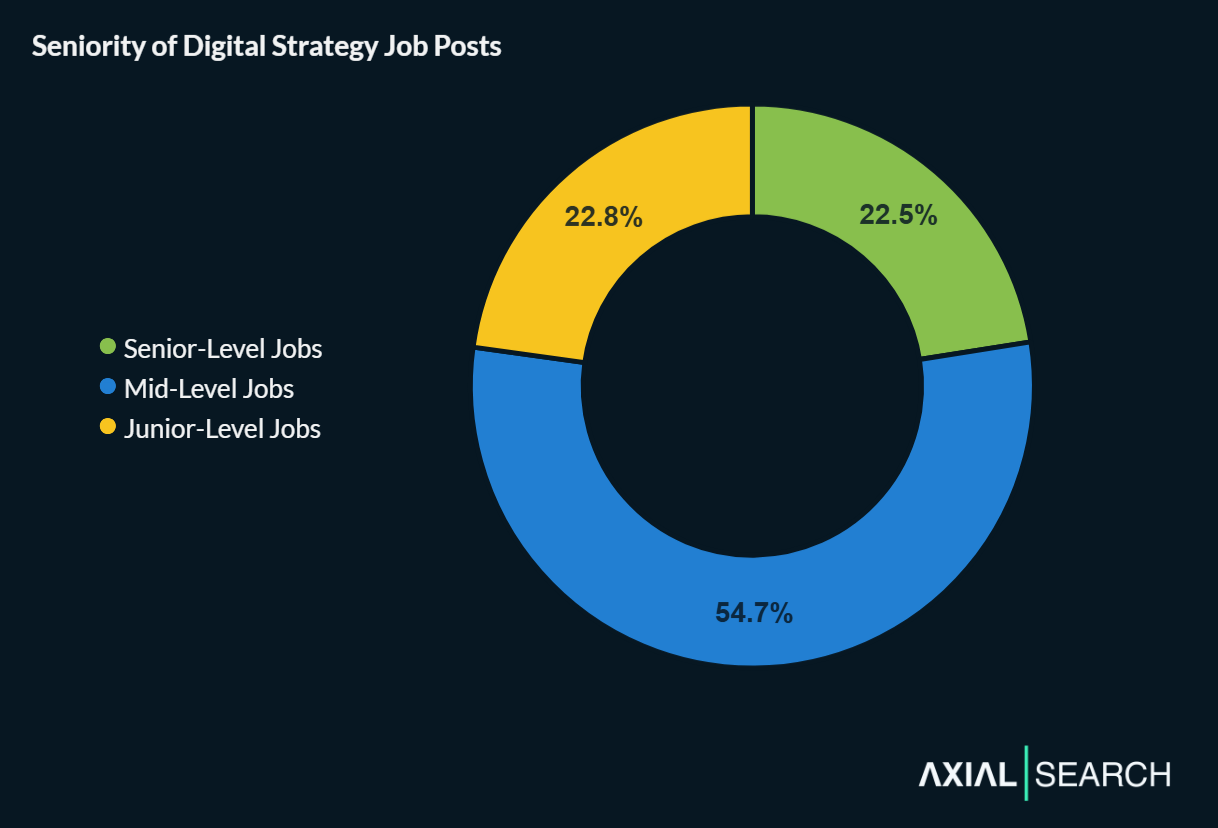
One quarter of digital strategy jobs are at the senior level
What Do Digital Strategy Jobs Involve?
So what is a digital strategy professional actually responsible for day-to-day? We analyzed the language across all job posts to extract the core responsibilities at each level. What emerged is a clear progression of expectations from execution to strategic vision:
Junior-Level Roles:
- Execute digital transformation initiatives from problem framing through roadmap design
- Build multi-channel campaigns across paid media platforms managing client relationships
- Implement domain-specific digital solutions for clinical workflows or e-commerce operations
Mid-Level Roles:
- Guide enterprise clients through complex technology decisions translating needs into roadmaps
- Own unified product strategies across organic growth, SEO and AI-driven discovery
- Lead partner evaluation and cross-functional execution for digital innovation initiatives
Senior-Level Roles:
- Own revenue and lead generation strategy across digital properties driving conversion optimization
- Define long-term vision for digital ecosystems, product portfolios or emerging technologies
- Build organizational capabilities through centers of excellence and strategic planning
Key takeaway: Junior strategists execute transformation initiatives, mid-level leaders own product strategies and guide clients, senior executives define organizational vision. Each step up means more influence over how digital capabilities shape the business.
Who’s Hiring for Digital Strategy?
Professional Services firms lead with 23% of digital strategy postings. Telecom & Media follows at 22%, with Financial Services rounding out the top three at 15%.
The concentration across these sectors reflects where digital transformation creates the most strategic value – consultancies advising enterprise clients, media companies adapting business models, and financial institutions modernizing customer experiences.
Technology captures 14%, with Healthcare at 4% completing the top five.
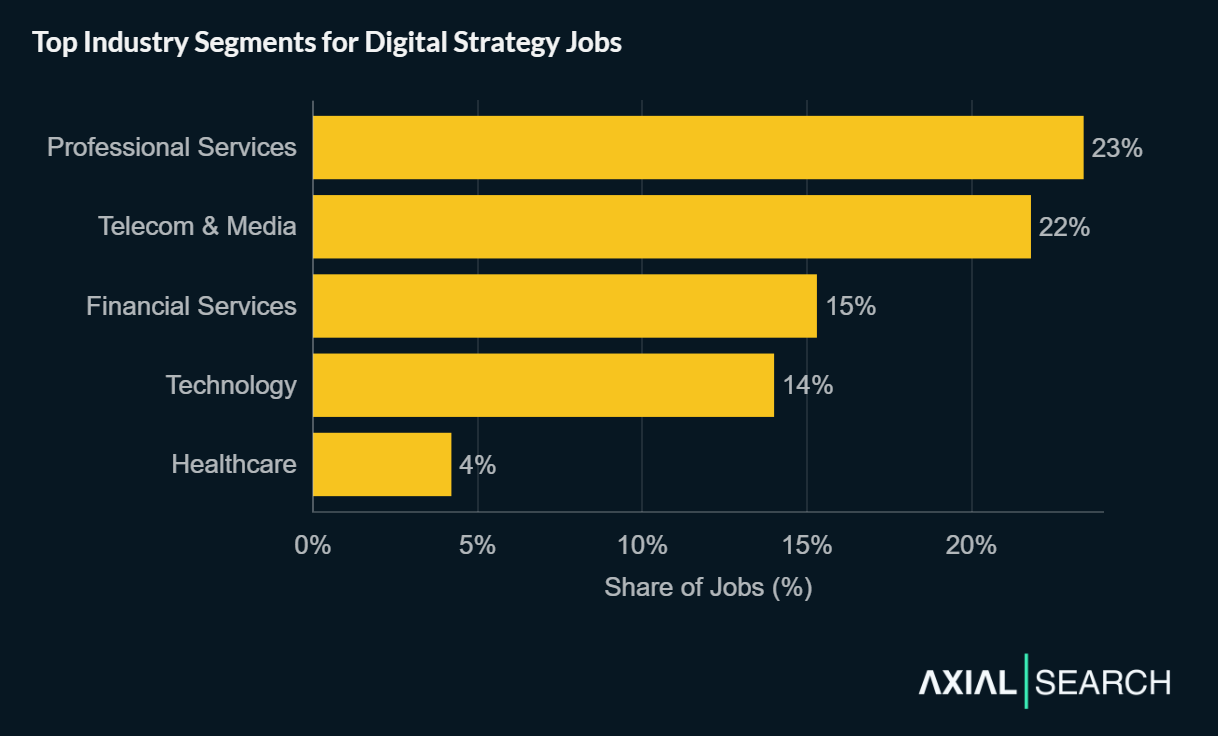
Service firms and media companies lead digital strategy hiring
Large companies with 10,001+ employees account for 40% of postings – above the broader workforce distribution across the U.S. economy. Organizations with 1,001-10,000 employees add another 18%, meaning roughly six out of ten digital strategy roles are at companies with over 1,000 employees.
What’s notable is the boutique presence – 17% of roles come from companies with fewer than 51 employees, likely representing specialized consultancies and agencies serving enterprise clients. This bimodal distribution suggests digital strategy serves both mature organizations building internal capabilities and specialized firms delivering transformation expertise.
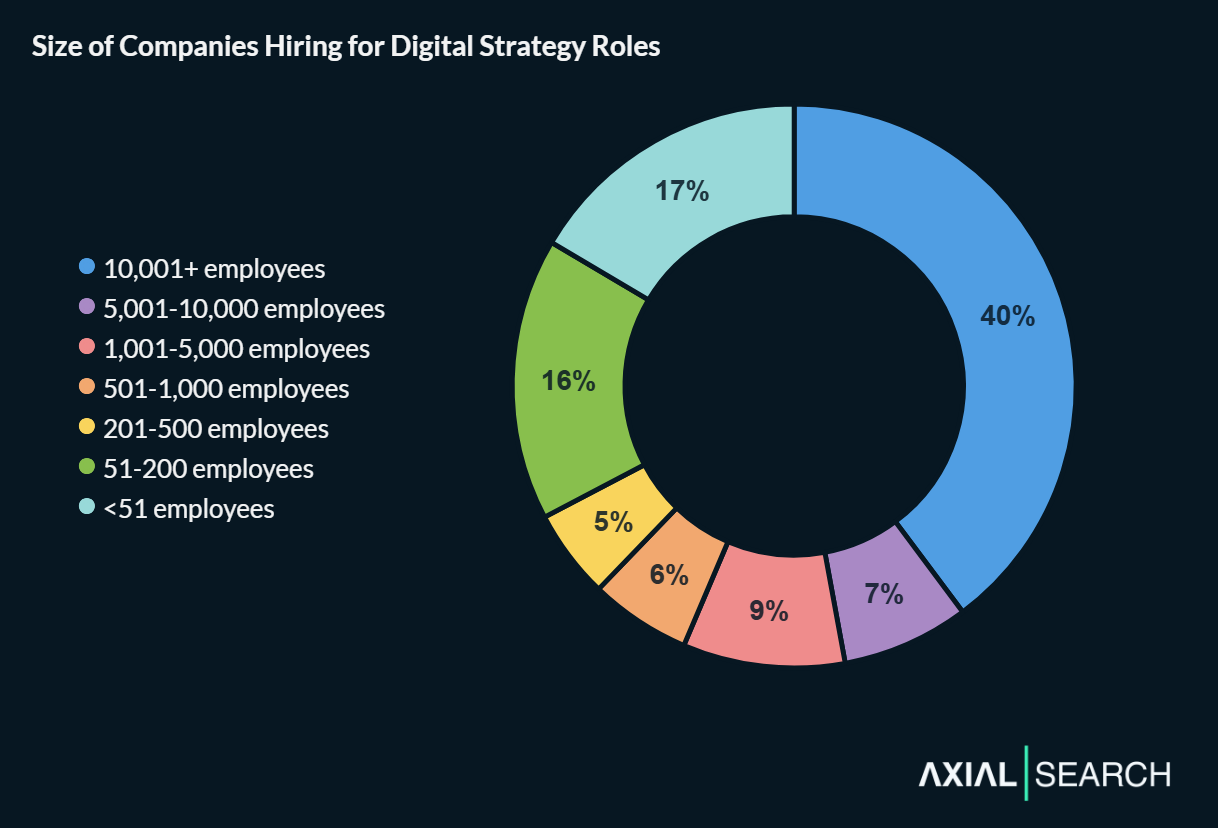
Large companies dominate but boutique firms are significant
Where Are Digital Strategy Jobs Located?
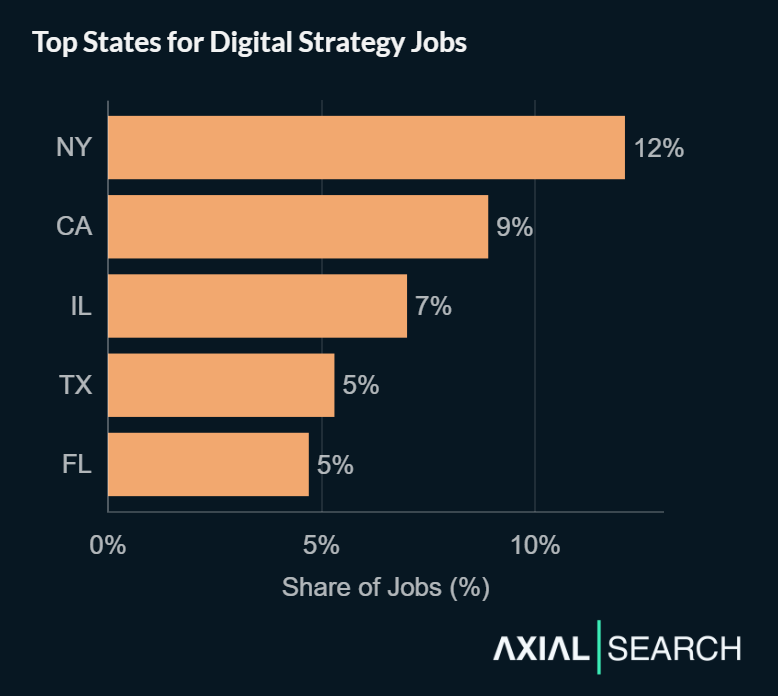
New York, California and Illinois lead digital strategy hiring
New York leads the market with 12% of all digital strategy postings. California follows at 9%, Illinois at 7%, Texas at 5%, and Florida rounds out the top five at 5%.
The concentration in major business hubs reflects where enterprise headquarters and consulting firms cluster. Remote roles account for just 10% of postings despite the strategic nature of the work, suggesting most organizations prefer digital strategists on-site where they can collaborate directly with executive leadership and cross-functional teams.
Beyond the top five, states worth watching include Virginia, Massachusetts, New Jersey and North Carolina – each capturing roughly 3-4% of the market and representing growing regional business centers with maturing digital transformation needs.
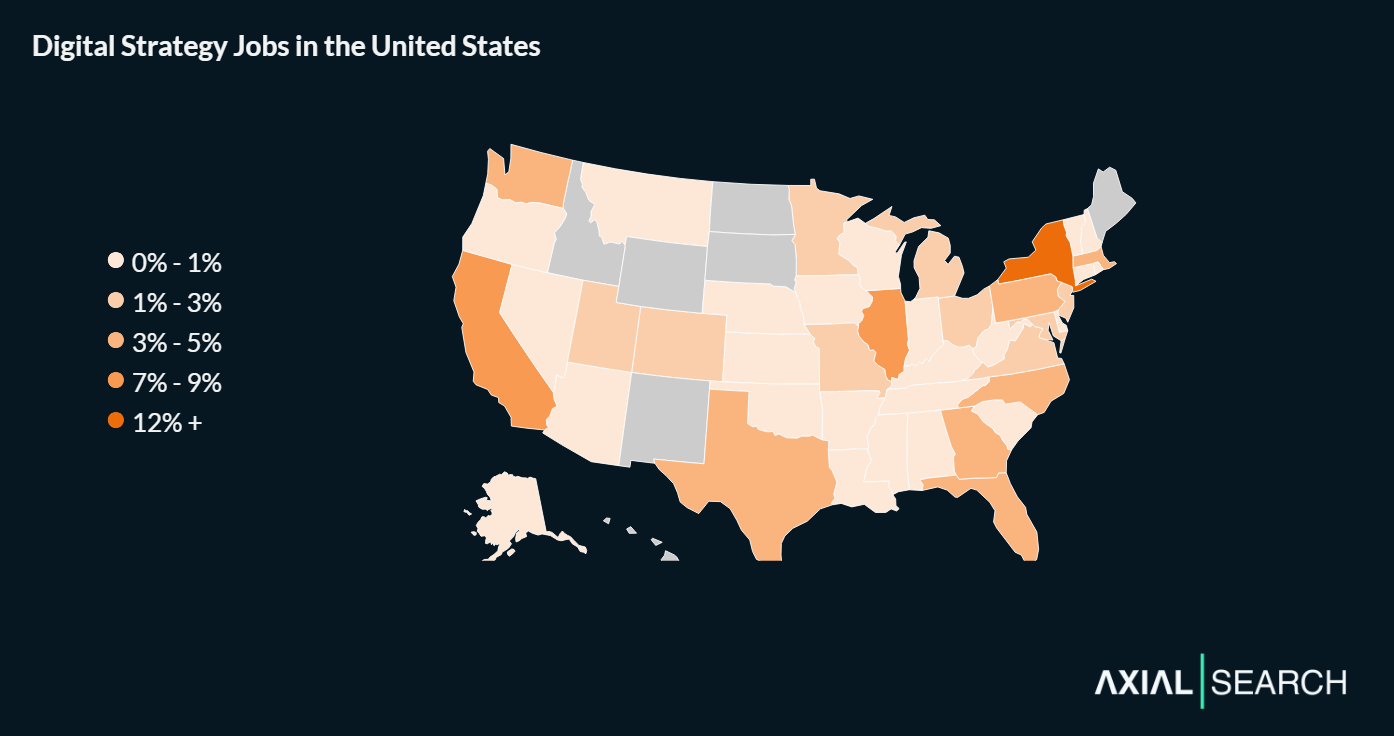
72% of digital strategy jobs are outside the top 3 states
Key takeaway: New York offers the most digital strategy opportunities by volume, but California and Illinois provide strong alternatives. The consultative nature of transformation work keeps remote options limited – expect hybrid or on-site requirements for most roles.
Requirements for Digital Strategy Jobs
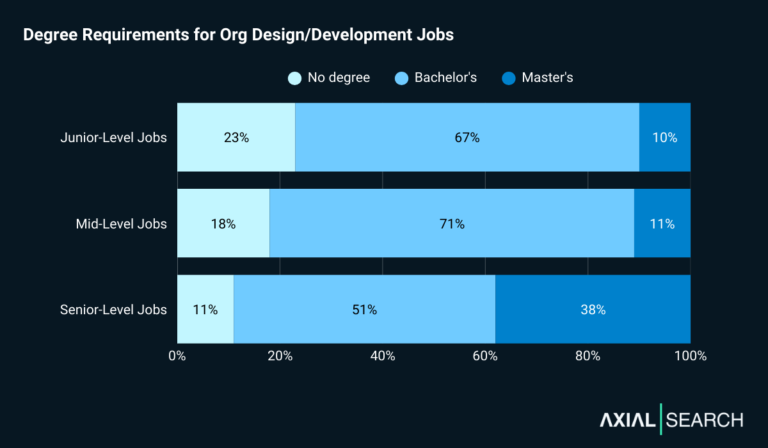
We analyzed the minimum requirements of each job post and found that most digital strategy jobs require some form of degree. What’s interesting is the pattern at senior levels – degree requirements actually loosen rather than tighten.
For junior roles, 68% require a degree (65% bachelor’s, 3% master’s). The remaining 32% don’t specify formal education requirements.
Mid-level positions show similar patterns: 70% require a degree (67% bachelor’s, 3% master’s).
Senior roles ease up: 56% require a degree (48% bachelor’s, 8% master’s).
The relaxation at senior levels suggests proven strategic impact eventually matters more than formal credentials – experience defining digital vision and driving measurable results trumps education.
Degree fields of study that are typically requested of digital strategists include:
- Marketing (16%)
- Business (13%)
- Communications (11%)
- Engineering (8%)
- Economics (7%)
- Business Administration (6%)
- Computer Science (6%)
- Finance (4%)
- Statistics (3%)
- Information Systems (2%)
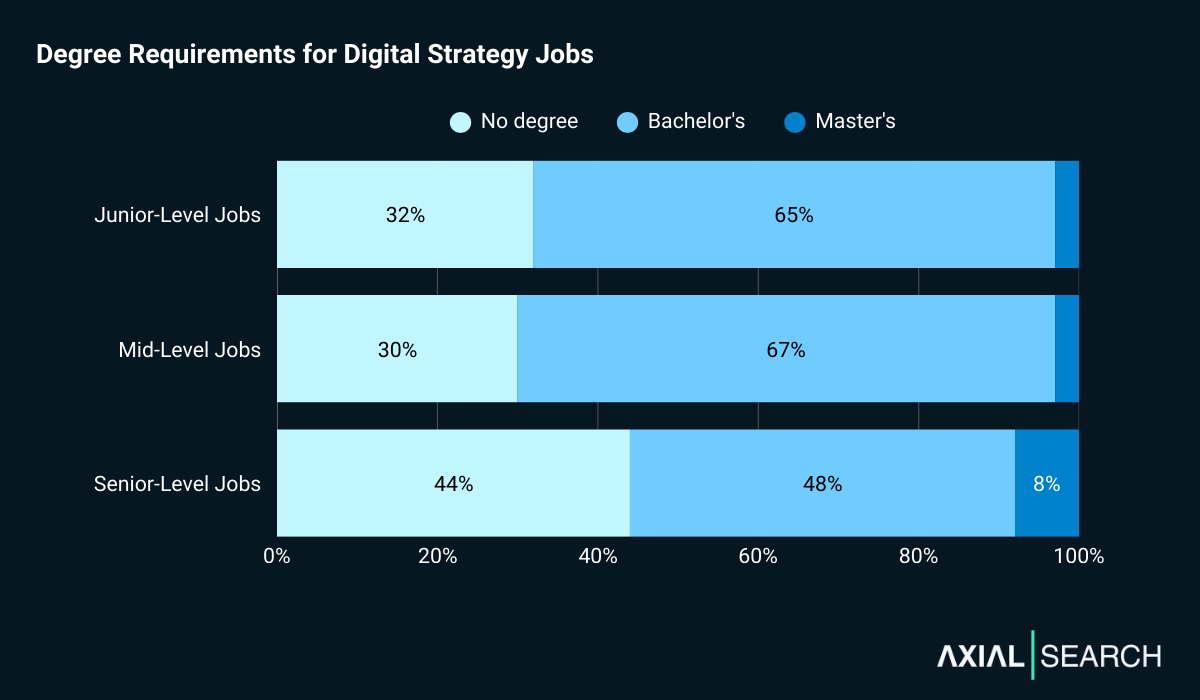
Degree requirements ease at senior levels
Requested Qualifications in Digital Strategy Job Posts
Digital strategists must excel at data analysis, communication and stakeholder management. Data analysis appeared in 45% of listings, communication in 27%, and stakeholder management in 23% – reflecting the role’s dual nature as both analytical problem-solver and organizational change agent.
Cross-functional collaboration (22%), stakeholder engagement (18%) and team leadership (17%) round out the core capabilities, emphasizing the need to orchestrate multiple teams while translating technical possibilities into business value.
Technical expertise matters equally. Project management (17%), technology strategy (15%) and business case development (14%) are table stakes, supported by hands-on experience with frameworks like Agile, TOGAF and Account-Based Marketing.
Just 7% of postings request specific certifications, but when they do, these credentials lead:
- Google Analytics Certification
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
- Google Ads Certification
- Meta Blueprint Certification
- Series 7 License
- Series 63 License
Key takeaway: Data fluency separates strong candidates from those who only understand business strategy. AI recruitment increasingly overlaps with digital strategy as organizations embed intelligence into customer experiences – analytical rigor paired with stakeholder management drives successful transformations.
What do Digital Strategy Jobs Pay?
Three out of five (60%) digital strategy roles we analyzed included an advertised salary.
There was significant breadth in the ranges employers posted, so we normalized the data by selecting the midpoint for our analysis. From our experience, this is generally a much more indicative number for an employer’s target offer – especially in the current market where initial ranges often run wide.
Across the entire dataset of salaries, we found the median salary for digital strategy positions to be $139,500. The middle 80% of salaries (10th to 90th percentile) ranged from $75,000 to $197,470.
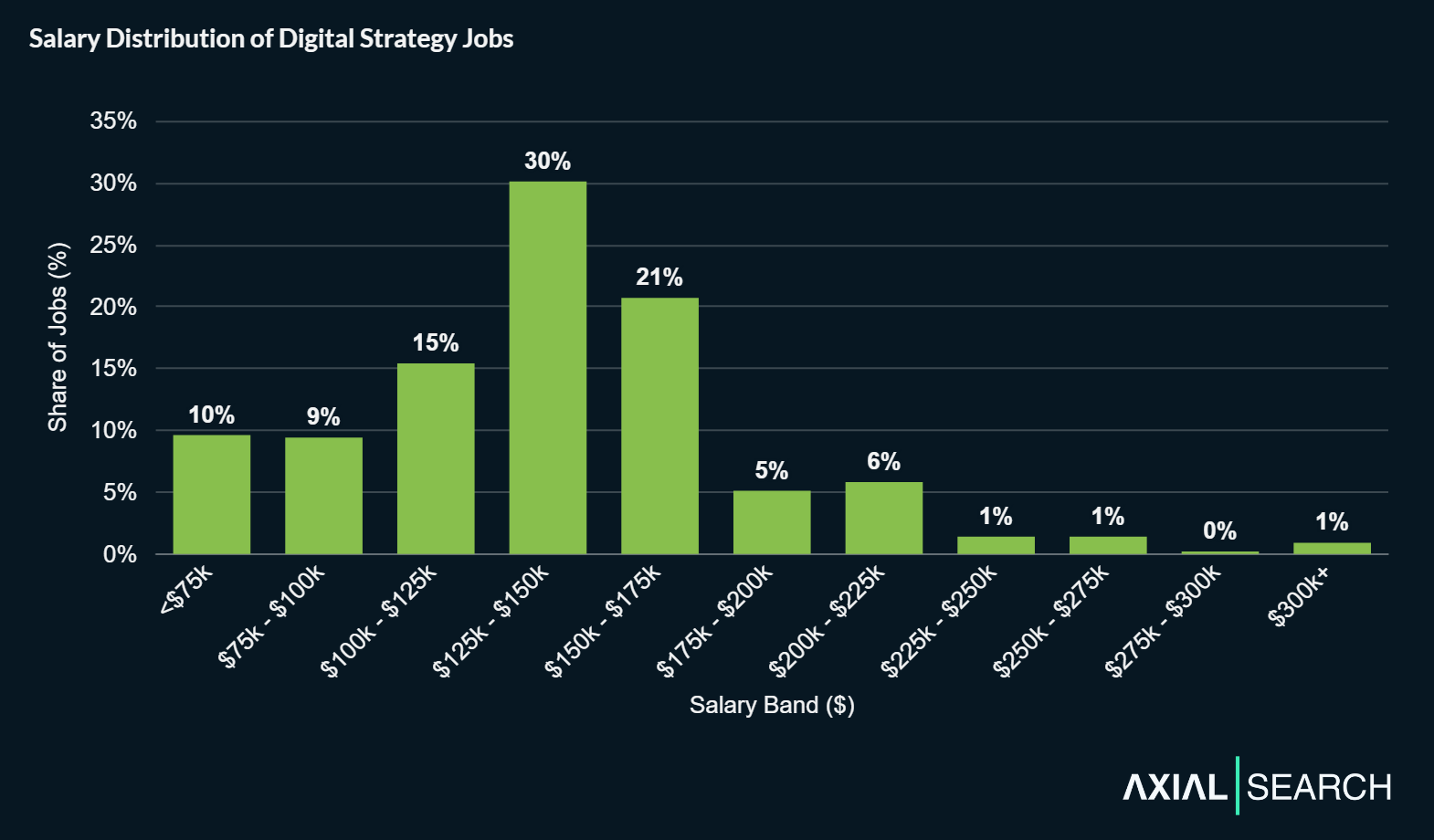
85% of digital strategy salaries are less than $175K
Breaking digital strategy salaries down by seniority reveals a curious pattern. Junior and mid-level roles show virtually no progression – junior median sits at $139,500 while mid-level climbs just 2% to $142,500. This minimal difference suggests title inflation at early career stages, where “strategist” labels often mask execution-focused work.
The real premium appears at senior levels – a 38% leap to $196,000 median. Senior roles also show the tightest clustering, with 75th percentile at $220,888 and 10th percentile at $129,900. This compression reflects how strategic accountability and revenue ownership command standardized premiums at leadership levels.
What’s striking is the junior salary range – clustering heavily at $139,500 across 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles. This suggests many entry-level “strategy” roles are actually standardized consulting positions with limited variation.
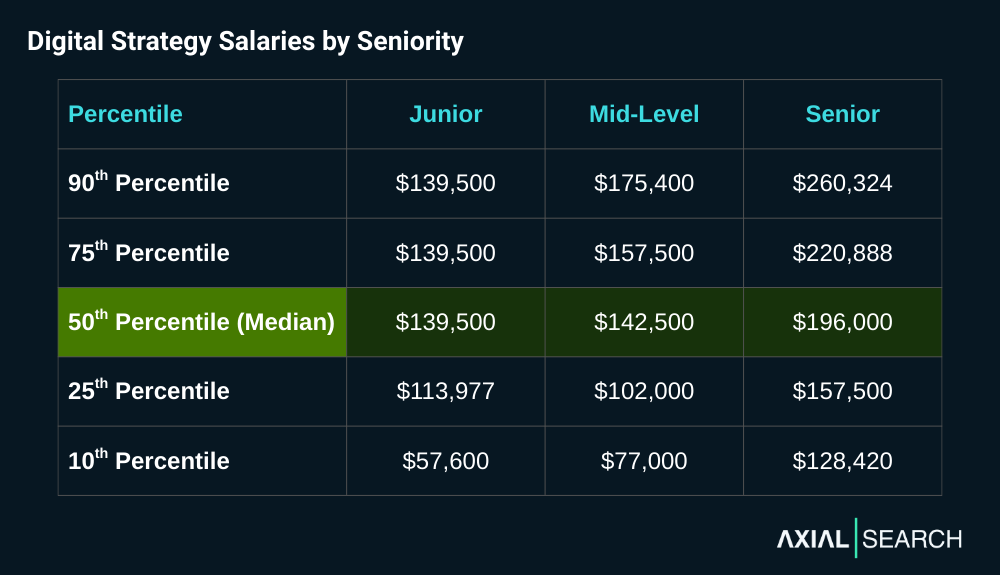
Senior digital strategists earn 38% more than mid-level professionals
Key takeaway: Digital strategy positions pay exceptionally well at senior levels. The median senior-level salary of $196,000 puts these roles in the top 7% of all earners in the United States. Even mid-level professionals earning the median $142,500 land in the top 13%.
Final Thoughts
For Candidates: Build hands-on experience with Google Analytics and paid media platforms early – these technical capabilities matter more than strategy frameworks alone. For mid-level roles, demonstrating you’ve owned unified product strategies that drove measurable performance separates candidates. At senior levels, experience defining digital vision and building organizational capabilities matters more than campaign execution. Google Analytics and PMP certifications accelerate credibility.
For Employers: The flat salary clustering around $140,000 for junior and mid-level roles reflects market confusion – many “strategist” titles mask execution work. For genuine strategic roles, expect to pay the senior premium. The strongest signal for senior candidates is experience driving revenue through digital properties and building transformation capabilities, not just advising on technology adoption. Remote flexibility remains limited despite strategic work – expect candidates to push for hybrid arrangements.
Methodology
We analyzed 1,002 digital strategy job postings collected from LinkedIn, Indeed and Glassdoor between November 2024 and January 2025. The dataset was limited to full-time roles posted in the United States that explicitly mentioned “digital strategy,” “digital strategist” or close variations in the job title.
Duplicate postings were removed using job title, company name and location matching. Seniority levels were determined by analyzing job titles alongside minimum experience requirements stated in each posting. When experience ranges were provided, the lower bound was used for consistency.
Salary data was extracted from the 60% of postings that included compensation ranges. We used the midpoint of each range for analysis, as this most closely reflects employer target offers in practice.
Industry classifications were assigned based on company descriptions and verified against LinkedIn company data where available. Geographic analysis was conducted at the state level using the primary job location listed in each posting.